Antidiabetic Activity of the Methanol Fraction of Sungkai Leaves (Peronema canescens Jack)
Abstract
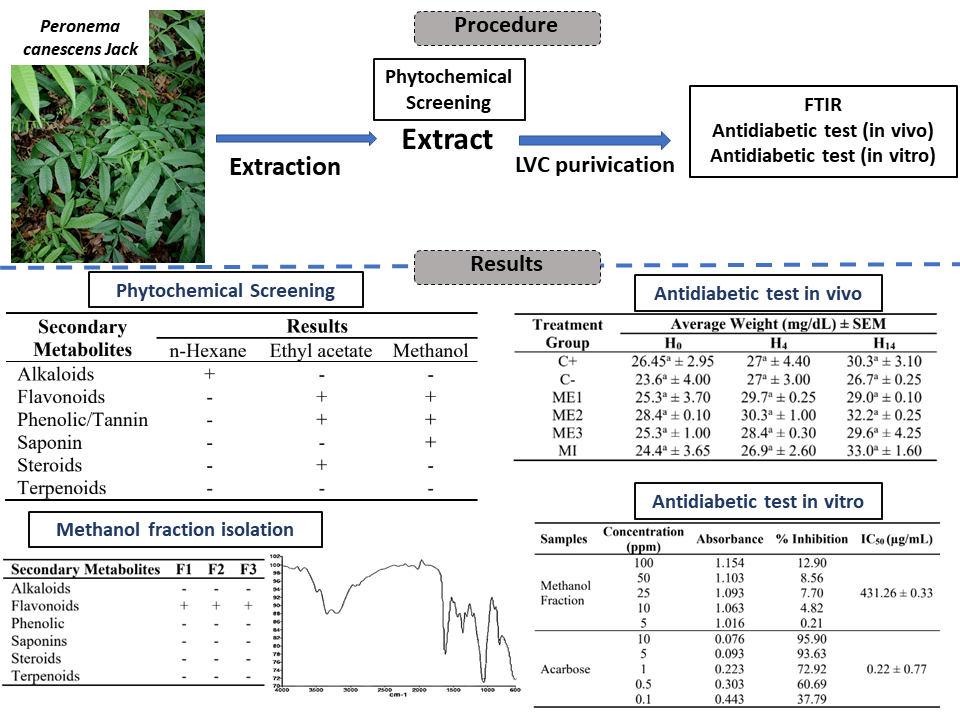
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is one of a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia caused by a disturbance in insulin so that blood glucose levels increase. Prevention of absorption of blood glucose by the intestine can be done with the help of the enzyme α-glucosidase. Based on the results of phytochemical tests, it is known that the methanol fraction of sungkai leaves contains flavonoid compounds. The Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) spectrum showed that the isolates had phenolic O-H groups (3,354.53 cm-1, 1,359.28 cm-1), aromatic C=C group (1,615.48 cm-1), C-O-C ether group (1,046.60 cm-1) and aromatic C-H group (822.21 cm-1). In vivo antidiabetic activity test was carried out using test animals of white male mice which were induced by alloxan. Antidiabetic testing was carried out using 6 treatment groups with glibenclamide, Na-Carboxymethyl cellulose (Na-CMC) 0.5%, dose 175 mg/kgBW, 350 mg/kgBW, 700 mg/kg Body Weight (BW) and isolates 2 mg/kgBW. The results showed that the methanol fraction of sungkai leaves had the best antidiabetic activity at a dose of isolate and 700 mg/kgBW which was able to reduce blood glucose levels by 42.20% and 42.00%. In vitro antidiabetic testing through α-glucosidase enzyme inhibition mechanism did not show any antidiabetic activity at concentrations of fractions 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 ppm.
References
[1] Galicia-Garcia, U., Benito-Vicente, A., Jebari, S., Larrea-Sebal, A., Siddiqi, H., Uribe, K.B., Ostolaza, H. and Martín, C., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(17), p.6275.
[2] Craig, M.E., Hattersley, A. and Donaghue, K.C., Pediatr Diabetes, 2009, 10(Suppl 12), pp.3-12.
[3] Arifin, H., Chou, K.R., Ibrahim, K., Fitri, S.U.R.A., Pradipta, R.O., Rias, Y.A., Sitorus, N., Wiratama, B.S., Setiawan, A., Setyowati, S. and Kuswanto, H., J. Multidiscip. Healthc., 2022, pp.2203-2221.
[4] Banday, M.Z., Sameer, A.S. and Nissar, S., Avicenna J. Med., 2020, 10(04), pp.174-188.
[5] S. Sinulingga, S., Subandrate, S. and Safyudin, S., Jurnal Kedokteran dan Kesehatan, 2020, 16(1), pp.76-83.
[6] Sari, S.G., Rahmawati, R., Rusmiati, R. and Susi, S., EnviroScienteae, 2023, 19(1), pp.35-40.
[7] Kusriani, R.H., Nawawi, A. and Turahman, T., Jurnal Farmasi Galenika, 2015, 2(1), pp.8-14.
[8] Andriani, F., Sundaryono, A. and Nurhamidah, N., Alotrop, 2017, 1(1), 33-38.
[9] Latief, M., Lizawati, L., Tarigan, I.L., Muhaimin, M. and Sari, P.M., AIP Conference Proceedings, 2023, 2595, 080004.
[10] Ahmad, I. and Ibrahim, A., Jurnal Sains dan Kesehatan, 2015, 1(3), pp.114-119.
[11] Prasiwi, D., Sundaryono, A. and Handayani, D., Alotrop, 2018, 2(1), 25-32.
[12] Fikriansyah, M., Latief, M. and Tarigan, I.L., CHEMPUBLISH JOURNAL, 2023, 7(1), pp.54-63.
[13] N. A. P. Pakpahan, “Isolasi dan Uji Aktivitas Antikolesterol Senyawa Metabolit Sekunder dari Fraksi n-Heksana Daun Sungkai (Peronema canescens Jack),” Bachelor Thesis, Sriwijaya University, Palembang, 2021.
[14] Tarigan, I.L., Aini, I.P.S. and Latief, M., Pharmacogn. J., 2022, 14(6), 744-752.
[15] Br, Sitepu N., Asian J.Pharm. Res. Dev., 2020, 8(3), pp.59-61.
[16] Z. A. Amani & R. Mustarichie, Farmaka, 2018, 16 (1), 127–132.
[17] Dillasamola, D., Aldi, Y., Wahyuni, F.S., Rita, R.S., Umar, S. and Rivai, H., Pharmacogn. J., 2021, 13(6), 1397-1407.
[18] Nuraskin, C.A., Idroes, R. and Soraya, C., Res. J. Pharm. Technol., 2019, 12(11), pp.5247-5250.
[19] Khalivulla, S.I., Mohammed, A. and Mallikarjuna, K., Curr. Pharm. Des., 2021, 27(6), pp.775-788.
[20] Kokalj Ladan, M., Straus, J., Tavčar Benković, E. and Kreft, S., Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), p.7226.
[21] Mahmiah, M., Indones. J. Chem., 2006, 6(3), pp.312-315.
[22] Al-Ishaq, R.K., Abotaleb, M., Kubatka, P., Kajo, K. and Büsselberg, D., Biomolecules, 2019, 9(9), p.430.
[23] Li, C.X., Li, T.H., Zhu, M., Lai, J. and Wu, Z.P., J. Funct. Foods., 2021, 85, p.104638.
[24] Kottaisamy, C.P.D., Raj, D.S., Prasanth Kumar, V. and Sankaran, U., Lab. Anim. Res., 2021, 37(1), pp.1-14.
[25] Zhang, M., Montroy, J., Sharma, R., Fergusson, D.A., Mendelson, A.A., Macala, K.F., Bourque, S.L., Schlechte, J.M., Eng, M.K., McDonald, B. and Gill, S.E., Crit. Care Explor., 2021, 3(6), p.e0433.
[26] Soares, J.M.D., Leal, A.E.B.P., Silva, J.C., Almeida, J.R. and de Oliveira, H.P., Pharmacogn. Mag., 2017, 13(52), p.639.
[27] Garcia-Molina, P., Garcia-Molina, F., Teruel-Puche, J.A., Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N., Garcia-Canovas, F. and Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L., Molecules, 2022, 27(10), p.3141.
[28] U. Hossain, A. K. Das, S. Ghosh, & P. C. Sil, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2020, 145, 111738.
[29] Rehani, P.R., Iftikhar, H., Nakajima, M., Tanaka, T., Jabbar, Z. and Rehani, R.N., J. Diabetes Res., 2019, 4267357.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.