Study of Hydrogen Sulfide Adsorption on Silica Gel with Triethanolamine layer
Abstract
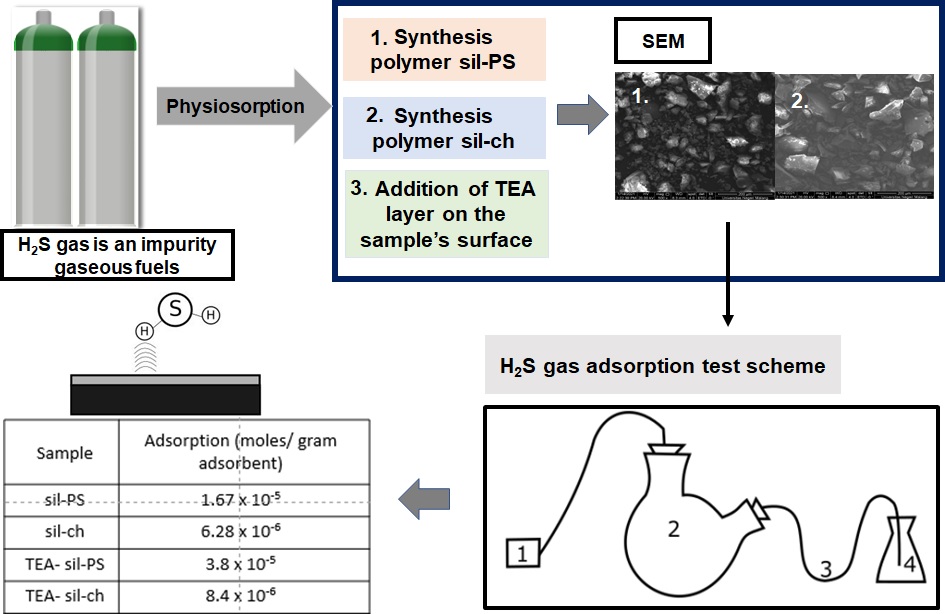
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is an impurity in gaseous fuels, therefore this gas removal method is interesting topic. Physisorption method is considered to a simple work to be applied on a small scale. The principle of physisorption is the combination of a substrate and a physical solvent to capture H2S gas. This research studies the impact of the addition of liquid triethanolamine on the porous silica on the adsorption capacity of H2S gas. The silica substrate is synthesized using two pore templates namely a mixture of polyethylene glycol (PEG)/ sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) and the other one is pure chitosan. Silica surface was coated with triethanolamine (TEA) using impregnation method. H2S gas adsorption study was conducted on the synthesized silica with and without TEA. The results of this study show that TEA layer on the silica surface increases the adsorption capacity towards H2S gas, but it is relatively small compared to similar studies. The best result of combining TEA and silica gel is shown by TEA- sil-PS which was 3.8 x 10-5 mol H2S per gram of adsorbent. The calculated surface area of the sil-PS is 6.64 m2/g or 98.6% reduction from the initial value 451.4 m2/g. The increase in adsorption capacity despite a very large decrease in surface area indicates the effectiveness of TEA in absorbing hydrogen sulfide.
References
[1] Strickland, J. US. EPA 2003, (CAS No. 7783-06-4)
[2] Georgiadis, A. G., Charisiou, N. D., Goula, M. A. Catalysts, 2020, 10 (5), 521.
[3] Bezerra, D. P., Oliveira, R. S., Vieira, R. S., Cavalcante, C. L., Azevedo, D. C. Springer Science, 2011, 235–246.
[4] Khabazipour, M., Anbia, M. I&E Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22133−22164.
[5] Okonkwo, C. N., Okolie, C., Sujan, A., Zhu, G., Jones, C. W. Energy and Fuels 2018, 32 (6), 6926–6933.
[6] Chu, X., Cheng, Z., Zhao, Y., Xu, J., Zhong, H., Zhang, W., Lü, J., Zhou, S., Zhu, F., Zhou, Y., Zhou, L. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51 (11), 4407–4413.
[7] Singh, L. P., Bhattacharyya, S. K., Kumar, R., Mishra, G., Sharma, U., Singh, G., Ahalawat, S. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 214, 17–37.
[8] Purwanto, A. S., Taslimah, T., Sriatun, S. J. Kim. Sains dan Apl. 2012, 15 (1), 1–6.
[9] Witoon, T., Chareonpanich, M. Mater. Lett. 2012, 81, 181–184.
[10] Lalchhingpuii, Tiwari, D., Lalhmunsiama, Lee, S. M. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 434–444.
[11] Handayani, P. A., Nurjana, E., Rengga, W. D. P. JBAT, 2015, 4 (2), 55–59.
[12] Najafi, M., Yousefi, Y., Rafati, A. A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 85, 193–205.
[13] Sari, L., Sudiarta, I. W., Putra, A.A.B. J. Kim, 2015, 9, 153–159.
[14] Newalkar, B. L., Komarneni, S. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2000, 18 (3), 191–198.
[15] Hammouda, B. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2013, 118, 151.
[16] Fouad, W. A., Berrouk, A. S. I&E Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6591−6597
[17] Zhang, H., Yang, C., Geng, Q., Fan, H., Wang, B., Wu, M. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497 (June), 143815.
[18] Han, Y., Hwang, G., Kim, H., Haznedaroglu, B. Z., Lee, B. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 653–662.
[19] Shen, Z., Cai, Q., Yin, C., Xia, Q., Cheng, J., Li, X., Wang, Y. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 217.
[20] Chen, Q., Fan, F., Long, D., Liu, X., Liang, X., Qiao, W., Ling, L. I&E Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11408–11414
[21] Zhong, L., Zhou, L. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5 (3), 339–342
[22] Anbia, M., Babaei, M. IJE Trans. B 2014, 11, 1697-1704
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.