Biosynthesis of Cu2O/CuO-NP and AgNP Using Rhizopus oligosporus as Reductor Agent
Abstract
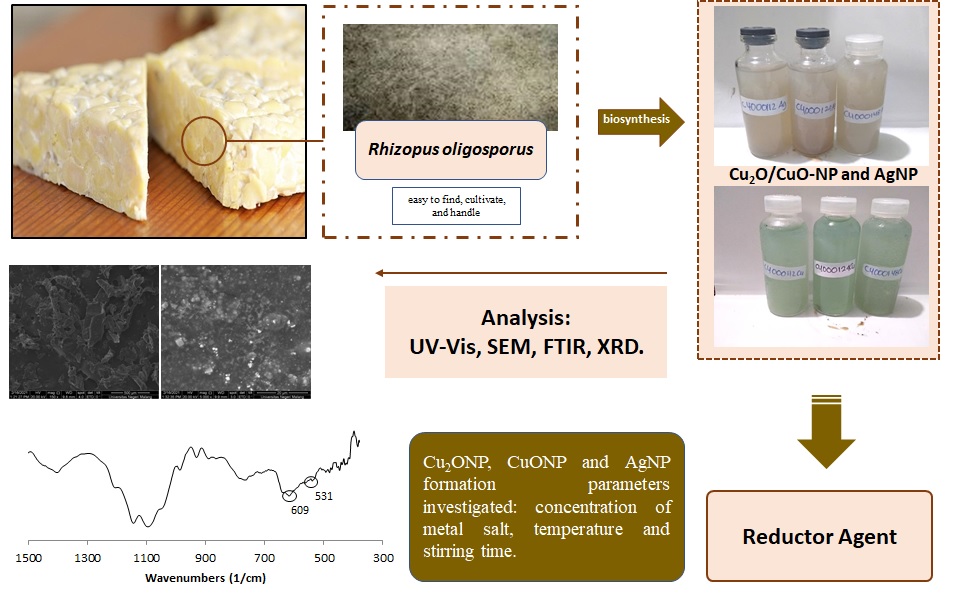
Nanoparticles have been widely used in various fields which depends on its size and shape. Nanoparticles can be synthesized physically and chemically. However, these methods need large amount of energy, not environmental friendly and quite expensive, because requires several additional materials besides precursors. In this study, we performed the analysis of some parameters to determine the best conditions for biosynthesis using Rhizopus oligosporus to obtain the nanoparticles with specific size. This fungi was used because easy to find, cultivate, and handle. We found that grain size of Cu2O/CuO-NP and AgNP obtained are 23 nm, 55 nm respectively. In conclusion, this study confirms that some parameters investigated and Rhizopus oligosporus can be used to obtain the nanoparticles with specific size.
References
[1] Iravani, S., Korbekandi, H., Mirmohammadi, S. V and Zolfaghari, B, Res Pharm Sci, 2014, 9 (6), 385.
[2] Oliveira, M. M., Ugarte, D., Zanchet, D and Zarbin, A. J, J.Colloid Interface Sci, 2005, 292 (2), 429–435.
[3] Luo, K., Jung, S., Park, K. H and Kim, Y. R. J. Agric. Food Chem, 2018, 66 (4), 957–962.
[4] AbdelRahim, K., Mahmoud, S. Y., Ali, A. M., Almaary, K. S., Mustafa, A. E. Z. M. A and Husseiny, S. M, Saudi J. Biol. Sci, 2017, 24 (1), 208–216.
[5] Korbekandi, H., Mohseni, S., Mardani Jouneghani, R., Pourhossein, M and Iravani, S, Artif Cells, Nanomed Biotechnol, 2016, 44 (1), 235–239.
[6] Jain, N., Bhargava, A., Majumdar, S., Tarafdar, J. C and Panwar, J, Nanoscale, 2011, 3 (2), 635–641.
[7] Fuku, X., Modibedi, M and Mathe, M, SN Appl. Sci, 2020, 2 (5), 1-15.
[8] Lu, M. C and Huang, C. H, Nanoscale Res. Lett, 2013, 8 (1),1-7
[9] Rai, R and Chand, D. K, J Chem Sci, 2020, 132 (1), 83.
[10] Venkatesham, M., Ayodhya, D., Madhusudhan, A., Kumari, A.S., Veerabhadram, G and Mangatayaru , K. A, J Clust Sci, 2014, 25 (2), 409–422.
[11] Tian, Y., Chang, B., Fu, J., Zhou, B., Liu, J., Xi, F and Dong, X, J. Solid State Chem, 2014, 212, 1–6.
[12] Alhumaimess, M. S., Essawy, A. A., Kamel, M. M., Alsohaimi, I. H and Hassan, H., Nanomaterials, 2020, 10 (4), 781.
[13] Wahyudi, A. Jurnal Redoks, 2018, 3 (1), 37-44.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.