DFT and Molecular Docking Investigation of Potential Anticancer Properties of Some Flavonoids
Abstract
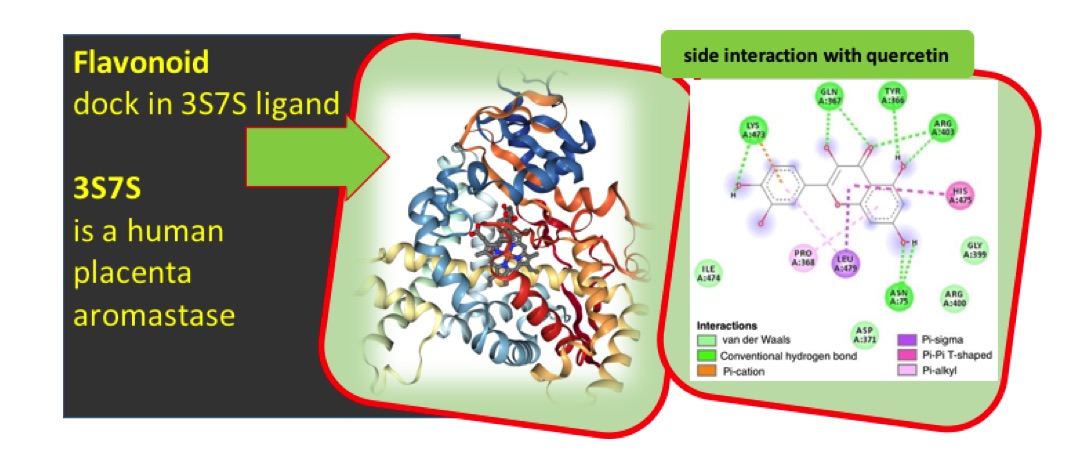
There is a continuous need to discover and obtain more efficient drug-like molecule to suppress cancer in human being. Recently researchers are using molecular docking technique to improve the understanding of the interaction between drug and receptor, in other to obtain novel drugs for more efficient usage. Anticancer activities of some selected flavonoids were studied using quantum chemical method through Density Functional Theory (DFT) and molecular docking approach. These Flavoniods were docked against breast cancer cell line (3s7s) using Autodock tool, AutoDockVina as docking tools and Biovia Discovery Studio 2017 for post docking analysis. The binding affinity obtained was used to correlate the inhibitory activity of these flavoniods with their calculated molecular descriptors. The obtained binding energy showed that quercetin has the highest inhibition efficiency hence it has the highest ability to inhibit 3s7s than other studied compounds. It was observed that some molecular descriptor such as band gap, dipole moment, logP and EHOMO, were significant to the inhibiting ability of quercetin in the active site of the protein.
References
[1]. Gibbs, J.B., Science., 2000, 287 (5460), 1969-1973.
[2]. Katrin Sak, and Hele Everaus, Curr Genomics., 2017, 18(1), 3-26.
[3]. Duraipandiyan Veeramuthu, William Raja Tharsius Raja, Naif Abdullah Al-Dhabi and Ignacimuthu Savarimuthu, Flavonoids in Anticancer Properties, 2017, 1st edition, InTech, 289-303.
[4]. Hira Iftikhar and Sajid Rashid, PHCOG MAG., 2014, 10(38), S264-S272
[5]. Panche, A.D., Diwan, A.D. and Chandra, S.R. J. Nutr. Sci., 2016, 5(47), 1–15.
[6]. Beecher, G.R., J Nutr., 2003, 133(10), 3248S-3254S.
[7]. Ren, W., Qiao, Z., Wang, H., Zhu, L. and Zhang, L., Med Res Rev., 2003, 23(4), 519-534.
[8]. Maheep, K.C., Neelu S., Mahabeer P.D. and Yogesh C.J., Pharmacogn Rev. 2011, 5(9), 1-12.
[9]. Priya Batra, and Anil K. Sharma, Biotech., 2013, 3(6), 439-459.
[10]. Gfeller, D., Grosdidier, A., Wirth, M., Daina, A., Michielin, O. and Zoete, V., Nucl. Acids Res., 2014, 42, 32-38.
[11]. Tewari, A.K., Singh, V.P., Yadav, P., Gupzxta, G., Singh, A., Goel, R.K., Shinde, P. and Mohan, C.G., Bioorg. Chem., 2014, 56, 8-15.
[12]. Choi, P. J. and Kim, B., J. Phy. Chem. B 2005 109,4333-4340
[13]. Xu, X., Shang, Z., Wang, G., Li, R., Caiand, Z. and Zhao, X., J. Phy. Chem. A., 2005 109, 3754-3761.
[14]. Bond, D., J. Phys. Chem. A., 2008. 112, 1656-1660.
[15]. Al-Otaibi, J. S. and Al-Wabli, R. I., Spectrochim Acta 2015, 137, 7-15.
[16]. Shashank Kumar, and Abhay Pandey, Sci World J., 2013, 1-16
[17]. Spartan 14, Wavefunction, INC, Irvine CA 92612, USA.
[18]. Becke, A.D., J. Chem. Phy., 1993, 98 (2), 5648-5652
[19]. Lee, C., Yang, W. and Parr, R.G., Phys. Rev. B., 1988, 37,785-789.
[20]. Ghosh, D. 2011, Crystal structure of human placental aromatase complexed with breast cancer drug exemestane DOI: 10.2210/pdb3S7S/pdb
[21]. Elfi Kraka, and Dieter Crèmer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122 (34), 8245–8264.
[22]. Mu, J.X., Zhai, Z.W., Yang, M.Y., Sun, Z.H., Wu, H.K. and Liu, X.H., Crystals, 2016, 6(4), 1-9.
[23]. Seminario, J.M., J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 1997, 37 (6), 1206-1206.
[24]. Taslı, P.T., Bayrakdar, A., Karakus, O.O., Kart, H.H., and Koc, Y., Opt. Spectrosc., 2015,119(3), 467-484.
[25]. Ibeji, U.I., Adejoro, I.A. and Adeleke B.B., Phys.Chem. Biophy., 2015, 5 (6), 1-11.
[26]. Hughes, J.D., Julian, B., David, P., Simon, B., Gary, A.D. and Rajesh, D., Bioorg. Med Chem. Lett., 2008, 18(17), 4872-4923.
[27]. Lipinski, C.A, Lombardo, F., Dominy, B.W. and Feeney, P.J., Adv. Drug Del. Rev., 2001 46, 3-26.
[28]. Almi, Z., Salah, B., Touhami, L. and Noureddine, T., ILCPA., 2014, 37, 113-124 [24]
[29]. Singh, Y.P. and Singh, R.A., Pak J Pharm Sci., 2008. 21(4), 390-395.
[30]. Meanwell, N., J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54(8), 2529-2591.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.