The Potential Role of Rosmarinic Acid and Sinensetin as α-Amylase Inhibitor: In Silico Study
Abstract
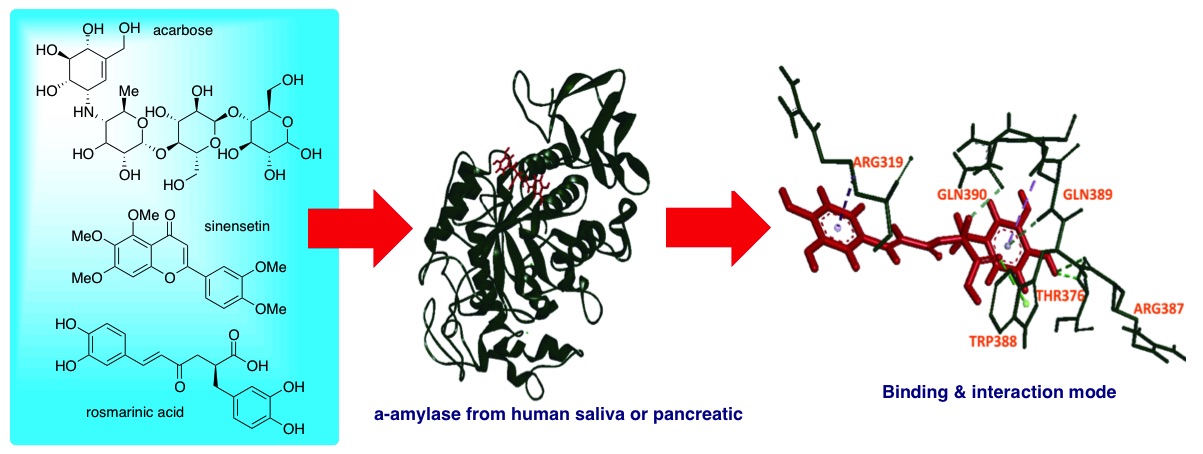
The study of natural compound as α-amylase inhibitor has been a concern since the synthetic drugs for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus have several side effects. The present study was carried out to predict the ability of rosmarinic acid and sinensetin as human α-amylase inhibitor by in silico study. All of the prepared 3D structures were used in the molecular docking by using Hex 8.0.0. The visualization of the molecular interactions of those compounds with human salivary α-amylase or human pancreatic α-amylase was established in the Discovery Studio Client 4.1 software. The result of this study determined that rosmarinic acid and sinensetin bound to the A domain of human pancreatic α-amylase and human salivary α-amylase. Rosmarinic acid-human salivary α-amylase complex was observed to possess high number of hydrogen bonds compared to sinensetin-human salivary α-amylase complex. The similar result was observed in the comparison of rosmarinic acid-human pancreatic α-amylase complex and sinensetin-human pancreatic α-amylase complex. The rosmarinic acid was able to bind the Glu233 of human pancreatic α-amylase. These data suggest rosmarinic acid as a potential inhibitor of human salivary α-amylase and human pancreatic α-amylase. Further experimental evidence is needed to confirm this observation.
References
[1] Butterworth, P. J., Warren, F. J., Ellis, P. R., Starch, 2011, 63, 395-405.
[2] Blanco, A., Blanco, G., Medical Biochemistry, 2017, Academic Press, London.
[3] Gerich, J., Int. J. Gen. Med., 2013, 6, 877–895.
[4] Krentz, A. J., Bailey, C. J., Drugs, 2005, 65 (3), 385-411.
[5] Rosak, C., Mertes, G., Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes., 2012, 5, 357–367.
[6] McCue, P. P., Shetty, K., Asia Pacific J. Clin. Nutr., 2004, 13 (1), 101–106.
[7] Ali, E., Mohamed, H., Jamshed, M., Siddiqui, A., Ang, L. F., Sadikun, A., Chan, S. H., Tan, S. C., Asmawi, M. Z., Yam, M. F. BMC Complement. Altern. Med.,. 2012, 12 (1), 1-7.
[8] Ngo, Y. L., Chua, L. S., Curr. Enzym Inhib., 2018, 14 (2), 97-103.
[9] Zhu, F., Asada, T., Sato, A., Koi, Y., Nishiwaki, H., Tamura, H., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62. 885-892.
[10] Kim, G., Park, Y. S., Jin, Y., Park, C., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 99, 2083–2092.
[11] Jhong, C., Riyaphan, J., Lin, S., Chia, Y., Weng, C., IUBMB, 2015, 41 (4) , 242–251.
[12] Hamdan, I., Afifi, F., Taha, M. O. Pharmazie, 2004, 59, 799-801.
[13] van der Maarel, M. J. E. C., van der Veen, B., Uitdehaag, J. C. M., Leemhuis, H., Dijkhuizen, L. J. Biotechnol., 2002, 94, 137–155.
[14] Brayer, G. D., Sidhu, G., Maurus, R., Rydberg, E. H., Braun, C., Wang, Y., Nguyen, N. T., Overall, C. M., Withers, S. G., Biochemistry, 2000, 39, 4778–4791.
[15] Brayer, G. D., Luo, Y., Withers, S. G., Protein Sci., 1995, 4, 1730–1742.
[16] Ramasubbu, N., Paloth, V., Luo, Y., Brayer, G. D., Levine, M. J., Acta Cryst., 1996, 435–446.
[17] Madeswaran, A., Asokkumar, K., Umamaheswari, M., Sivashanmugam, T., Subhadradevi, V., Jagannath, P., JCMMD, 2014, 4 (2), 51–56.
[18] de Sales, P. M., de Souza, P. M., Simeoni, L. A., Magalhães, P. D. O., Silveira, D., J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci., 2012, 15 (1), 141–183.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.