Effect of Dilution and Electrolysis Time on Recovery of Mg2+ As Mg(OH)2 from Bittern by Electrochemical Method
Abstract
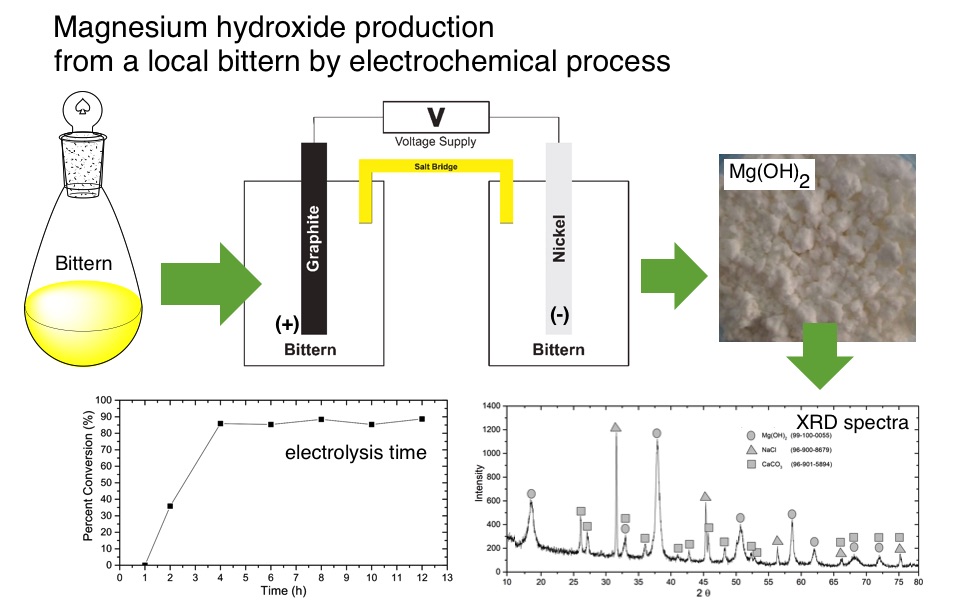
This research was conducted to study the effect of dilution and electrolysis time on therecovery of Mg2+as Mg(OH)2from bittern by electrochemical method. The electrochemical process was carried out using 2-compartment electrochemical cell, connected by salt bridge prepared from NaCl suspended in gelatin. The experiment was carried out using nickel as cathode and carbon as an anode. The electrolysis process was carried out at a potential of 18 volts with dilution factors of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 times, and electrolysis time of 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 hours. The results show that percent of conversion increased with dilution with the best result was obtained at 4x dilution factor and 4 hours electrolysis time with percent conversion of 85 % and purity of Mg(OH)291%
References
[1] Kuda, T., Yano, T., Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2014, 172 (6), 2989–2997.
[2] Seki, H., Hamada-Sato, N., J Aquac Mar Biol, 2014, 1 (1), 00001.
[3] Seki, H., Osako, K., Hamada-Sato, N., Int Food Res J, 2014, 21 (6), 2215–2220.
[4] Albuquerque, L. F., Salgueiro, A. A., Melo, J. L. de S., Chiavone-Filho, O., Sep Purif Technol, 2013, 104, 246–249.
[5] Ayoub, G. M., Hamzeh, A., Semerjian, L., Desalination, 2011, 273 (2–3), 359–365.
[6] Ayoub, G. ., Merhebi, F., Acra, A., El-Fadel, M., Koopman, B., Water Res, 2000, 34 (2), 640–656.
[7] Li, Y., Luo, W., Li, G., Wang, K. and Gong, X., Bioresour. Technol., 2018, 250, 53-59.
[8] Femitha, R. D., Vaithyanathan, C., Asian J Res Chem, 2013, 6 (12), 1099–1102.
[9] Li, X. Z., Zhao, Q. L., Environ Technol, 2002, 23 (9), 989–1000.
[10] Yaoting, L., J Salt Lake Res, 2009, 17 (2), 13–20.
[11] Ghara, K. K., Korat, N., Bhalodia, D., Solanki, J., Maiti, P., Ghosh, P. K., RSC Adv, 2014, 4 (65), 34706–34711.
[12] Abdullah, W. R., Mustafa, A. M. K., Iraqi Bull Geol Min, 2013, 9 (3), 129–146.
[13] Lozano, J. A. F., Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev, 1976, 15 (3), 445–449.
[14] El Rafie, S., Mohamed, M., Pelagia Res Libr, 2013, 4, 69–81.
[15] Mastuli, M., Kamarulzaman, N., Nawawi, M., Mahat, A., Rusdi, R., Kamarudin, N., Nanoscale Res Lett, 2014, 9 (1), 134.
[16] Dong, C., Cairney, J., Sun, Q., Maddan, O. L., He, G., Deng, Y., J Nanoparticle Res, 2010, 12 (6), 2101–2109.
[17] Gibson, A., Maniocha, M., Martin Marietta Magnesia Spec LLC, white Pap, 2004, 7.
[18] Miyakawa, H., Fujii, H., Okada, M., Shimatani, T., In 16th World Petroleum Congress; World Petroleum Congress,2000.
[19] Jakić, J., Labor, M., Martinac, V., Chem Biochem Eng Q, 2016, 30 (3), 373–379.
[20] Yamagata, C. & Paschoal, J. O. A., Materials Science Forum, 2014, 805, 712-717.
[21] Alamdari, A., Rahimpour, M. R., Esfandiari, N., Nourafkan, E., Chem Eng Process, 2008, 47 (2), 215–221.
[22] Amrulloh, H., Simanjuntak, W., Situmeang, R. T. M., ALKIMIA Journals Chem Appl Sci, 2017, 1 (1), 10–15.
[23] Park, J.-W., Lee, W.-K., Lee, C.-H., Mol Cryst Liq Cryst, 2016, 636 (1), 142–148.
[24] Hsu, G.-S. W., Lu, Y.-F., Hsu, S.-Y., J Food Drug Anal, 2017, 25 (4), 759–765.
[25] Gong, M., Wang, D.-Y., Chen, C.-C., Hwang, B.-J., Dai, H., Nano Res, 2016, 9 (1), 28–46.
[26] Hsu, S.-Y., J Food Eng, 2005, 66 (2), 171–176.
[27] Hanlon, J. M., Diaz, L. B., Balducci, G., Stobbs, B. A., Bielewski, M., Chung, P., MacLaren, I., Gregory, D. H., CrystEngComm, 2015, 17 (30), 5672–5679.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.