Development of Chlorpyrifos Sensor Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)-Fe3O4 as Receptor
Abstract
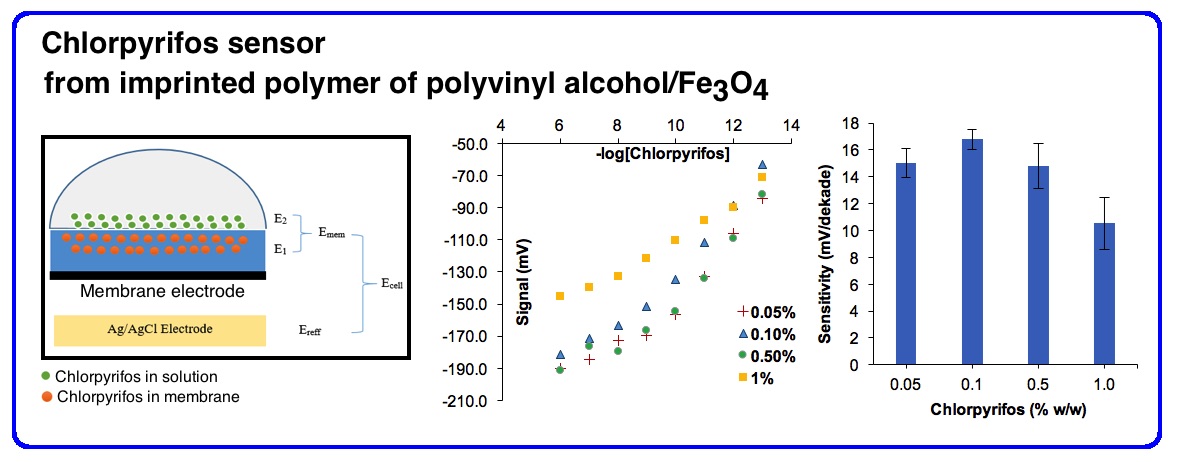
Development of a chemical sensor to detect chlorpyrifos has been carried out using a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-Fe3O4 as a membrane receptor. The MIP-Fe3O4 receptor is composed of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) polymer, glutaraldehyde crosslinking reagent, citric acid catalyst, chlorpyrifos template, and Fe3O4. The MIP-Fe3O4 receptor is coated on the working surface of the screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) with a size of 1.5 x 3 mm2. In this study, the effect of adding concentrations of chlorpyrifos and citric acid into membrane receptor was studied. The chlorpyrifos concentrations applied were 0.05, 0.1, 0.5 and 1% (w/w) and the concentrations of citric acid were 9.2, 16.8 and 23.3% (w/w). Sensor performance is also influenced by pH and type of electrolyte. The best sensitivity of the sensor is produced in the concentration range of 10-13 - 10-6 M at 24 mV/decade with a response time of 150 seconds.
References
[1] Eggins, B. R. Analytical Techniques in the Science - Chemical Sensor and Biosensor, 2004, John Wiley & Sons, England.
[2] Wang, J. Analytical Electrochemistry, 2006, Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Singapore.
[3] Pretsch, E., Badertscher, M., Welti, M., Maruizumi, T., Morf, W. E., Simon, W., Pure App. Chem. 1988, 60 (4), 567–574.
[4] Liang, R. N., Gao, Q., Qin, W., Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40 (3), 354–358.
[5] Javanbakht, M., Fard, S. E., Mohammadi, A., Abdouss, M., Ganjali, M. R., Norouzi, P., Safaraliee, L. Anal. Chim. Acta., 2008, 612 (1), 65–74.
[6] Smolinska-Kempisty, K., Ahmad, O. S., Guerreiro, A., Karim, K., Piletska, E., Piletsky, S. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 49–54.
[7] Najafi, M., Mehdipour, R. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3 (2), 132–137.
[8] Liang, R., Zhang, R., Qin, W. Sensor. Actuat., B-Chem. 2009, 141 (2), 544–550.
[9] Uchendu, C., Ambali, S. F., Ayo, J. O., Afr. J. Agric. Res., 2012, 7 (18), 2720-2728.
[10] Indonesia National Standard (SNI) 7313:2008, Batas maksimum residu pestisida pada hasil pertanian, 2008, Badan Standarisasi Nasional, Jakarta.
[11] Li, S., Ge, Y., Piletski, S. A., Lunec, J. Molecularly Imprinted Sensors : Overview and Applications, 2012, First edition, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
[12] Xu, W., Wang, Q., Huang, W., Yang, W. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40 (24), 4839–4846.
[13] Li, S., Liang, R., Qin, W., Yao, R. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10 (2), 1393–1403.
[14] Patachia, S., Friedrich, C., Florea, C., Croitoru, C., Express Polym. Lett., 2011, 5(2), 197–207.
[15] Wu, N. L., Wang, S. Y., Han, C. Y., Wu, D. S., Shiue, L. R. J. Power Sources 2003, 113 (1), 173–178.
[16] Abdallah, N. A., Ibhrahim, H. F., Hegabe, N. H. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12 (11), 10894–10910.
[17] Duan, G. W., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Xu, Y. M., Yin, F., Fu, Y. Z. Inorg. Nano. Met. Chem. 2017, 47 (4), 481–487.
[18] Kumar, N., Goyal, R. N., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 164 (6), B240–B246.
[19] Jayakrishnan, P., Ramesan, M. T. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2017, 27 (1), 323–333.
[20] Parkash, O., Yean, C. Y., Shueb, R. H. Diagnostics 2014, 4 (4), 165–180.
[21] Sridach, W., Jonjankiat, S., Wittaya, T. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27 (15), 1727–1738.
[22] Shitanda, I., Komoda, M., Hoshi, Y., Itagaki, M., Analyst 2015, 140(9), 6481-6484.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.