Extraction of Sodium Alginate from Sargassum sp. using Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
Abstract
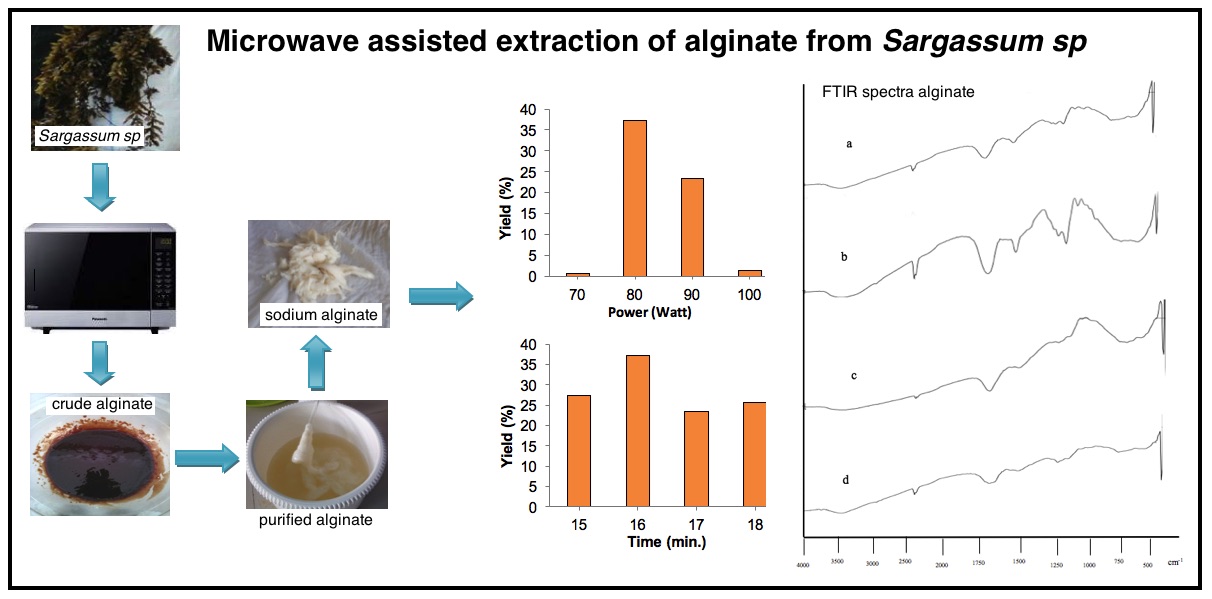
The method used in alginate extraction has been using conventional heating. Lately, Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) has been widely used to extract active compounds from natural ingredients. This study aims to extract sodium alginate from Sargassum sp. using MAE method. This research was conducted by determining the optimum power level and extraction time using a commercial microwave. Power level optimization is carried out at level 70; 80; 90 and 100, while extraction time is carried out for 15; 16; 17 and 18 minutes. The results showed that sodium alginate products were obtained at levels 70, 80, 90 and 100, respectively 0.5%; 37.13%; 23.36% and 1.2%. While sodium alginate products are obtained at variations in extraction time for 15; 16; 17 and 18 minutes were obtained respectively 27.4%; 37.13%; 26.1% and 25.76%. The characterization of sodium alginate products was carried out by analysis of water content, ash content, brightness, and viscosity in the sequence obtained by 14.43%; 14.63%; 78.62 and 95.00 cps. The results of the analysis of heavy metal content obtained that the product of sodium alginate extracted did not contain metal Pb and Hg. FTIR spectra results showed the presence of hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups at wave numbers 3448.7 cm-1 and 1620.21 cm-1; C-H bond at 2931.8 cm-1; alkene group at 2337.7 cm-1; sodium (Na) bond at 1419.61 cm-1; carbonyl group at 1095.57 cm-1 and carboxylic and ketone groups at 1033.85 cm-1. Based on the results of the characterization proving that the product obtained is a sodium alginate compound.
References
Amir, H., Subaryono, Pranoto, Y., Tazwir dan Ustadi, Agritech, 2012, 32(1), 1-8. [2] Mushollaeni, W., Afr. J. Food Sci., 2011, 5(6), 349–352. [3] Silva, M., Gomes, F., Oliveira, F., Morais, S., Matos, C.D.. Int. J. Chem., Nucl., Matter. Metallurgical Eng., 2015, 9(1), 30-33. [4] Jain, T., Jain, V., Pandey, R., Vyas, A., & Shukla, S., Asian J. Res. Chem. 2009. 2(1), 19-25. [5] Mandal, V., Mohan, Y., & Hemalatha, S. Pharmacogn Rev. 2007. 1(1). 7-18. [6] Ghallisa, K.N., Nugroho, W.A., Hendrawan, Y., Jurnal Bioproses Komoditas Tropis, 2014, 2 (1), 72-78. [7] Handayani, D., Mun’im, A., Ranti, A.S., Trad. Med. J., 2014, 19 (1), 29-35. [8] Kartikasari, D., Wardhani, D.H., Prasetyaningrum, A., Jurnal Teknik Kimia, 2013, 19(3), 38-43. [9] Rafiee, Z. S. M., Jafari, M., Alami, Khomeiri, J. Anim. Plant Sci., 2011, 21(4), 738-745. [10] Amir, A., Wiraningtyas, A., Ruslan, dan Annafi, N, Chempublish Journal, 2016, 1(2), 7-13. [11] AOAC, Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemistry, 15th Edition, 1990, Washington, 456-579. [12] James, CS., Analytical Chemistry of Foods, 1995, Blackie Academic and Profesional, London, 80-95. [13] Silverstein, R.M. Webster, F.X. Kiemle, D.J., Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 8th edition, 2005, Jhon Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 79-80. [14] Fertah, M., Belfkira, A., Dahmane, E.M., Taourirte, M., Arab. J. Chem., 2017, 10 (Supplement 2), S3707-S3714. [15] Fauziah, F., Aulani’am, A., Mahdi, C., J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2013, 2(3), 102-107.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.