Potential of Anthocyanin From Purple Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) To Increase BDNF Level and VEGF Expression in The Cerebellum of Ischemic Stroke Rats
Abstract
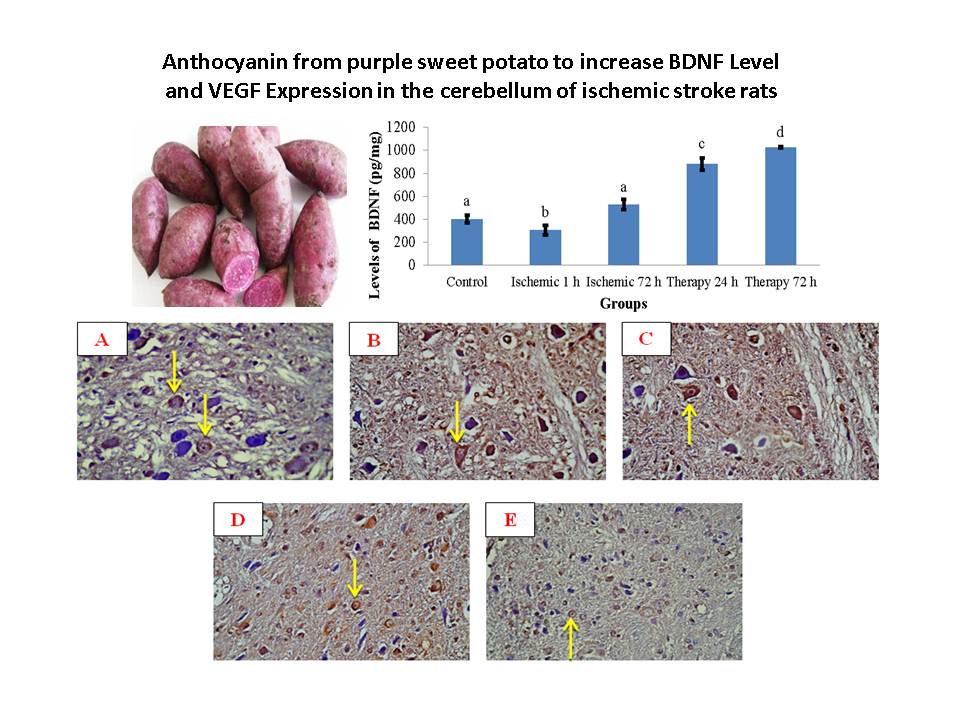
This research studies the effect of anthocyanin from purple sweet potato in the cerebellum of stroke ischemic rats by MCAO (Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion) technique. This technique was carried out by ligating the blood flow in ECA and CCA region for 3 hours, followed by reperfusion. The MCAO technique proved as a technique for preparing ischemic stroke rats. This technique induces releasing of BDNF and VEGF in the cerebellum of ischemic stroke rats. The level of BDNF measured by ELISA technique and VEGF expression used immunohistochemistry technique. The results showed that anthocyanin from purple sweet potato increased the level of both BDNF and VEGF expression in the cerebellum in ischemic stroke rats. It is suggested that anthocyanin could be used as a therapeutic agent for ischemic stroke.
References
[1] X. He, X. Li, Y. Lv, and Q. He, Food Sci. Technol, 2015, 35(3). website
[2] I. Suda, T. Oki, M. Masuda, and M. Kobayashi, JARQ, 2002, 37(3), 167–173. website
[3] J. Zhao, Q. Yan, L. Lu, and Y. Zhang, Nutr Res Pract., 2013, 7(5), 359–365. crossref
[4] Y. Pil, J. Ho, E. Hee, H. Gyun, and J. Wee, Nutr. Res., 2011, 31(12), 896–906. crossref
[5] Z. Zhang, J. Lu, Y. Zheng, D. Wu, B. Hu, Q. Shan, W. Cheng, M. Li, and Y. Sun, J. Nutr. Biochem., 2013, 24(6), 1008–1018. crossref
7] Y. P. Hwang, J. H. Choi, J. M. Choi, Y. C. Chung, and H. G. Jeong, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2011, 49(9), 2081–2089. crossref
[8] H. Sun, T. Mu, X. Liu, M. Zhang, and J. Chen, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62(11), 2364–2373. website
[9] Y. Wang, Y. Zheng, J. Lu, G. Chen, X. Wang, J. Feng, J. Ruan, X. Sun, C. Li, and Q. Sun, Neurochem. Int., 2010, 56(3), 424–430. crossref
[10] X. Chen and K. Wang, Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 2016, 6(6), 522–530. crossref
[11] Charleston and R. J. Adam, Ischemic Stroke Therapeutics: A Comprehensive Guide, 2016, Springer, Switzerland.
[12] S. Ma, H. Zhao, X. Ji, and Y. Luo, Exp. Neurol., 2015, 272, 41-49. crossref
[13] C. An, Y. Shi, P. Li, X. Hu, Y. Gan, R. A. Stetler, R. K. Leak, Y. Gao, B. Sun, P. Zheng, and J. Chen, Prog. Neurobiol., 2014, 115, 6–24. crossref
[14] R. A. Wardle and M. Poo, J Neurosci, 2003, 23(25), 8722–8732. crossref
[15] S. Bürger, Y. Yafai, M. Bijl, P. Wiedemann, and R. Schliebs, Int J Dev Neurosci, 2010, 28(7), 597–604. crossref
[16] K. L. Jin, X. O. Mao, and D. A. Greenberg, Proc Nati Acad Sci S A.,2000, 97(18), 10242-102427. crossref
[17] Adnyana IMO, Sudewi AAR, Sumatra DPGP, Suprapta ND, Aulanni’am A., Bali Med J, 2017, 6(1), 156–160.
[18] R. Setin and C. Mahdi, J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2013, 2, 55–61. crossref
[19] L. P. Gina and C. Mahdi, J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2016, 5, 40–47. website
[20] A. Chan, J. Yan, P. Csurhes, J. Greer, and P. Mccombe, J. Neuroimmunol, 2015, 286, 42–47. crossref
[21] N. Bertrand, P. Garnier, and C. Marie, Neurochem. Int., 2011, 58 (1), 102–111. crossref
[22] K. W. Wu, P. Yang, S. S. Li, C. W. Liu, and F. Y. Sun, Neuroscience, 2015, 298, 94–101. crossref
[23] V. Della Mea, G. L. Baroni, D. Pilutti, and C. Di Loreto, PLoS ONE, 2017, 12 (7) ,1–9. website
[24] David A. Greenberg, Cell Mol Life Sci., 2014, 70 (10), 1753–1761. website
[25] X. Yao, W. Miao, M. Li, M. Wang, J. Ma, Y. Wang, L. Miao, and H. Feng, Neurosci. Lett., 2011, 472 (3), 179–183. crossref
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.