Optimization Of Elevating Blood Uric Acid Levels With High Purine Diet
Abstract
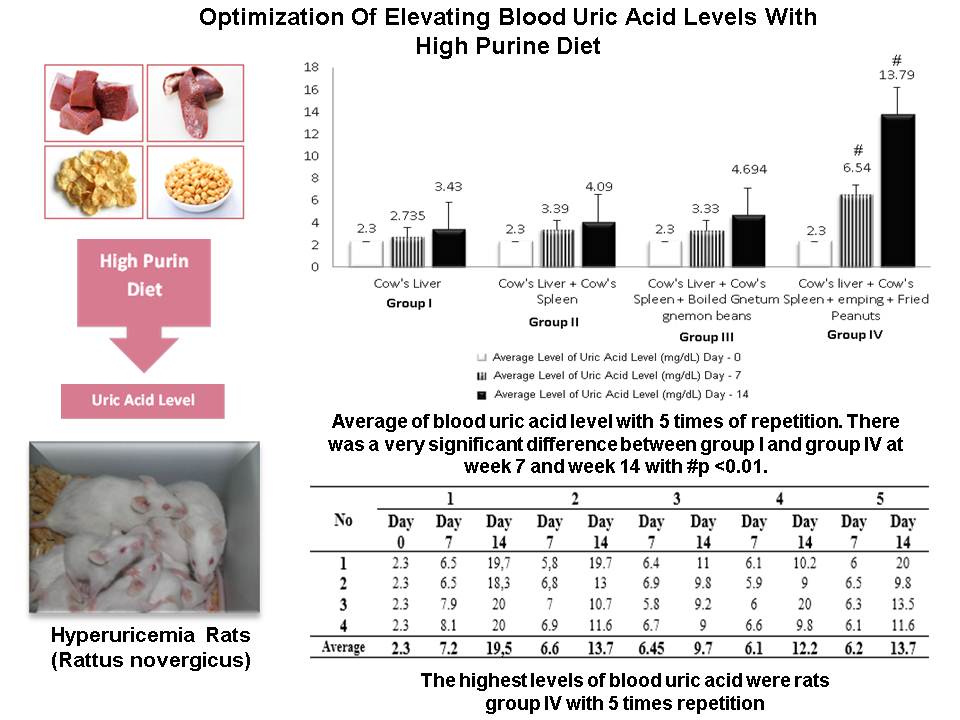
Exploration of the use of medicinal plants to lower uric acid levels has been widely practiced. Stages of new drug development research is a preclinical test using experimental animals, therefore the manufacture of an animal model of hyperuricemia is necessary. This study aims to determine the optimal induction of uric acid to increase blood uric acid levels by administering high purine foods such as cow’s liver, cow’s spleen, Gnetum gnemon, emping and fried peanuts. Eighty male white rats were used individuals to be divided into 4 groups, they were: (I) cow’s liver, (II) cow’s liver and cow’s spleen, (III) cow’s liver, cow’s spleen and boiled gnetum gnemon beans, and (IV) cow’s liver, cow’s spleen, emping and fried peanuts. This study using easy touch GCU to measure blood uric acid level. The result of statistical analysis of uric acid level means with 5 times repetition using One Way ANOVA showed that there was a very significant difference between treatments (p <0,01). The results concluded that high purine diet in group I, II and III had not been able to increase uric acid levels significantly. High purine diet group IV was able to increase blood uric acid levels significantly to make the rats experiencing hyperuricemia with the level of 6.54 mg/dL on day 7 and 13.79 mg/dL on day 14.
References
[1] Torralba, K.D, De Jesus, E., and Rachabattula, S., 2012, Int. J. Rheum. Dis., 15(6), 499–506. website
[2] Yamanaka, H., 2012, Japan Med. Assoc. J., 55, 4, 324–329. website
[3] Maiuolo, J., Oppedisano, F., Gratteri, S., Muscoli, C., and Mollace, V., 2016, Int. J. Cardiol., 213, 8–14. crossref
[4] Gliozzi, M., Malara, N., Muscoli, S., and Mollace, V., 2016, Int. J. Cardiol., 213, 23–27. crossref
[5] Choi, H. K, Mount, D. B, and Reginato, A. M, 2005, Ann. Intern. Med., 143(7), 499–516. website
[6] Baker, J. F, and Shumacher, H. R, 2010, Int. J. Clin. Pract., 53(3), 557–558. website
[7] Al-azzawie, H. F, and Abd, S. A, 2015, Int. J. Adv. Res., 2(6), 55–61. website
[8] Werner, A. K, and Witte, C. P, 2011, Trends Plant Sci., 16(7), 381–387. crossref
[9] Zhao, X., Zhu, J. X, Mo, S. F, Pan, Y., and Kong, L. D, 2006, J. Ethnopharmacol., 103, 357–365. crossref
[10] Manuaba, P., 2012, Adv. Pure Appl. Chem., 2(1), 86–90, 2012.
[11] NHS, N., “Dietary Advice for People with Gout,”2017, Dep. Nutr. Diet. Norfolk Norwich Univ. Hosp. NHS Found. Trust James Paget Univ. Hosp. NHS Found. Trust, no. November, pp. 1–2.
[12] Kaneko, K., Aoyagi, Y., Fukuuchi, T., Inazawa, K., and Yamaoka, N., 2014, Biol Pharm Bull., 37, 709–721. website
[13] Settaluri, V. S, Kandala, C. V., Puppala, N., and Sundaram, J., 2012, Food Nutr. Sci., 2012, 1644–1650. website
[14] Gowda, S., Desai, P. B, Kulkarni, S. S, Hull, V. V, Math, A. K, and Vernekar, S. N, 2010, N. Am. J. Med. Sci., 2(4), 170–3. website
[15] With, T., and Versus, F., 2014, Prof. Med. J., 59.
[16] A. K. Pathak, V. Pathak, L. E. Seitz, W. J. Suling, R. C. Reynolds, 2004, J Med Chem 1, 273–276. website
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.