Green Tea Extract (Camellia sinensis L.) Effects on Uric Acid Levels on Hyperuricemia Rats (Rattus norvegicus)
Abstract
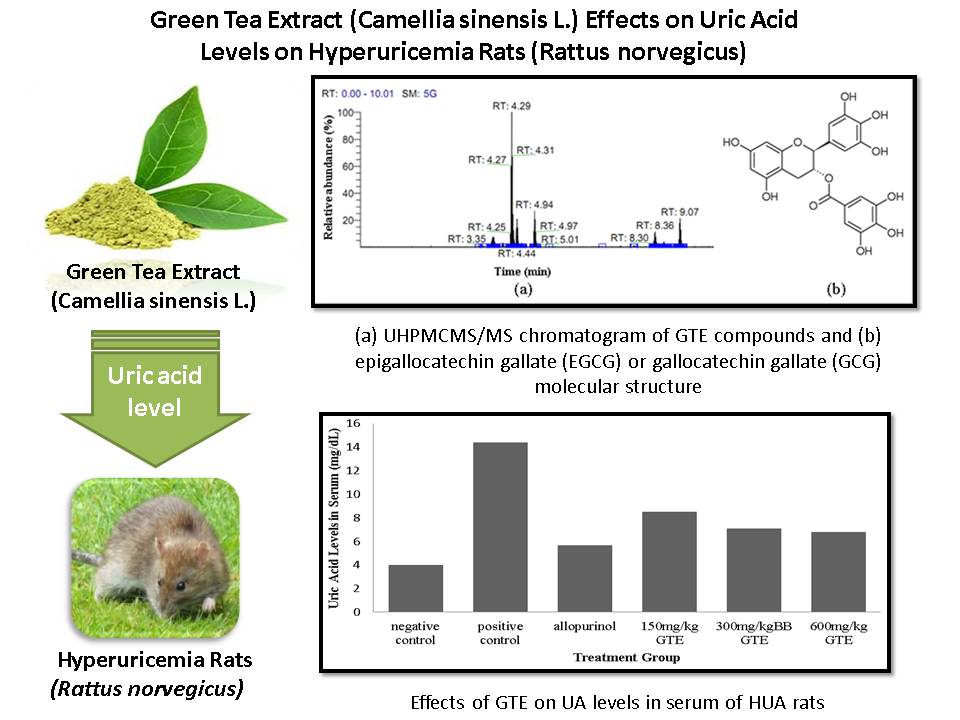
Uric acid is the end product of purine degradation. When uric acid levels exceed normal limits, it will build up and cause hyperuricemia. Allopurinol is one of the most effective and common medicine for hyperuricemia, but it brings serious side effects, therefore it is needed alternative therapy for hyperuricemia. One plant that may be expected to low uric acid levels is green tea (Camellia sinensis L.), that contains many antioxidants polyphenols, especially flavonoids. Flavonoid has strong antioxidant properties, act as free radical and metal scavengers, and also xanthine oxidase (XOD) inhibitors. This study investigates the potential of green tea using various doses of 150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg, and 600 mg/kg of body weight in 24 white male rats (Rattus norvegicus) Wistar strain that has been received high purine diet in 60 consecutive days. This study used DHBSA methods to measure uric acid levels in blood serum and urine that excreted 8 hours before surgery. Green tea extract that contains polyphenol can inhibit XOD activities, therefore, it leads to decrease uric acid level in blood and increase the excretion through urine by modulating urate gene transporter. A therapy with 600 mg/kg body weight of GTE is the most effective dose to decrease uric acid levels in serum and to increase excretion of exceeding uric acid significantly (p < 0.01), from One Way ANOVA and Tukey analysis.
References
[1] G. Lippi, M. Montagnana, M. Franchini, E. J. Favaloro, and G. Targher, Clin. Chim. Acta, 2008, 392(1–2), 1–7.
[2] L. A. Baldree M. D. and F. B. Stapleton M. D., Pediatr. Clin. North Am., 1990, 37(2), 391-418.
[3] D.-H. Kang, T. Nakagawa, L. Feng, S. Watanabe, L. Han, M. Mazzali, L. Truong, R. Harris and R. J. Johnson, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2002, 13(12), 2888–2897.
[4] M. E. Balis, Uric Acid Metabolism in Man. 1984, The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
[5] P. Cirillo, W. Sato, S. Reungjui, M. Heinig, M. Gersch, Y. Sautin, T. Nakagawa and R. J. Johnson, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2006, 17(12), S165-S168.
[6] H. M. Kramer and G. Curhan, Am. J. Kidney Dis., 2002, 40, 1, 37–42.
[7[ A. N. Rohma, C. Mahdi, and A. Aulanni’am, J. Pure Appl. Chem. Res., 2017, 6(2), 160–165.
[8] D. I. Feig and R. J. Johnson, Hypertension, 2003, 42(3), 247–252.
[9] D. I. Feig, B. Soletsky, and R. J. Johnson, JAMA, 2008, 300(8), 924–32.
[10] D. Astuti, Efek Antihiperurisemia Kombinasi Ekstrak Air Kelopak Rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) dan Akar Tanaman Akar Kucing (Acalypha indica L.) Pada Tikus Putih Jantan yang Diinduksi Putih Jantan yang Diinduksi Kalium Oksonat, Department of Pharmacy, University of Indonesia, Indonesia, 2011.
[11] H. K. Choi and G. Curhan, Arthritis Rheum., 2007, 57(5), 816–821.
[12] C. G. Fraga, M. Galleano, S. V. Verstraeten, and P. I. Oteiza, Mol. Aspects Med., 2010, 31(6), 435–445.
[13] G. Chen, M. L. Tan, K. K. Li, P. C. Leung, and C. H. Ko, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2015, 175, 14–20.
[14] D. Bolignano M.D., G. Coppolino M.D., A. Barillà M.D., S. Campo M.D., M. Criseo M.D., D. Tripodo M.D., M. Buemi M.D., J. Ren. Nutr., 2007, 17(4), 225–234.
[15] P. J. Rogers, J. E. Smith, S. V Heatherley, and C. W. Pleydell-Pearce, Psychopharmacology (Berl)., 2008, 195, 569–577.
[16] T. Kakuda, A. Nozawa, T. Unno, N. Okamura, and O. Okai, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2000, 64, 2, 287–293.
[17] K. Kaneko, Y. Aoyagi, T. Fukuuchi, K. Inazawa, and N. Yamaoka, Biol. Pharm. Bull., 2014, 37(5), 709–721.
[18] D. Brulé, G. Sarwar, and L. Savoiet, J. Food Compos. Anal., 1988, 1(2), 130–138.
[19] H. K. Choi, S. Liu, and G. Curhan, Arthritis Rheum., 2005. 52, 1, 283–289.
[20] M. H. O’Regan, J. W. Phillis, and G. A. Walter, Neurochem. Int., 1989, 14, 1, 91–99.
[21] K. Jatuworapruk, S. Srichairatanakool, S. Ounjaijean, N. Kasitanon, S. Wangkaew, and W. Louthrenoo, J. Clin. Rheumatol., 2014, 20, 6, 310–3.
[22] A. Rashidinejad, E. J. Birch, and D. W. Everett, J. Food Compos. Anal., 2016, 48, 120–127.
[23] K. Boudiaf, Z. Houcher, S. Widad, and M. Benboubetra, JABS, 2010, 4(1), 7–16.
[24] T. Hayashi, K. Sawa, M. Kawasaki, M. Arisawa, M. Shimizu, and N. Morita, J. Nat. Prod., 1988, 51(2), 345–348.
[25] F. Preitner, A. Laverriere-Loss, S. Metref, A. D. Costa, C. Moret, S. Rotman, D. Bazin, M. Daudon, C. Sandt, A. Dessombz, B. Thorens, Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol., 2013, 305, 5, F786-95.
[26] M. S. Lipkowitz, Curr. Rheumatol. Rep., 2012, 14(2), 179–188.
[27] X.Wu, D. M. Muzny, C. C. Lee, and C. T. Caskey, J. Mol. Evol., 1992. 34(1), 78–84.
[28] P. H. F. Gois, D. Canale, R. A. Volpini, D. Ferreira, M. M. Veras, V. Andrade-Oliveira, N. O. S. Câmara, M. H. M. Shimizu, A. C. Seguro, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2016, 101, 176–189.
[29] R. A. Shaw, S. Kotowich, H. H. Mantsch, and M. Leroux, Clin. Biochem., 1996, 29, 1, 11–19.
[30] A. Enomoto, H. Kimura, and A. Chairoungdua, Nature, 2002, 417, 447–452.
[31] K. Ichida, H. Matsuo, T. Takada, A. Nakayama, K. Murakami, T. Shimizu, Y. Yamanashi, H. Kasuga, H. Nakashima, T. Nakamura, Y. Takada, Y. Kawamura, H. Inoue, C. Okada, Y. Utsumi, Y. Ikebuchi, K. Ito, M. Nakamura, Y. Shinohara, M. Hosoyamada, Y. Sakurai, N. Shinomiya, T. Hosoya, and H. Suzuki, Nat. Commun., 2012, 3, 764, 1-7.
[32] A. So and B. Thorens, J. Clin. Invest., 2010, 120, 6, 1791–1799.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.