Potential Cassava Skin Waste (Manihot esculenta C.) In the Production of Bioethanol by Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Fermentation Using Zymomonas mobilis Bacteria
Abstract
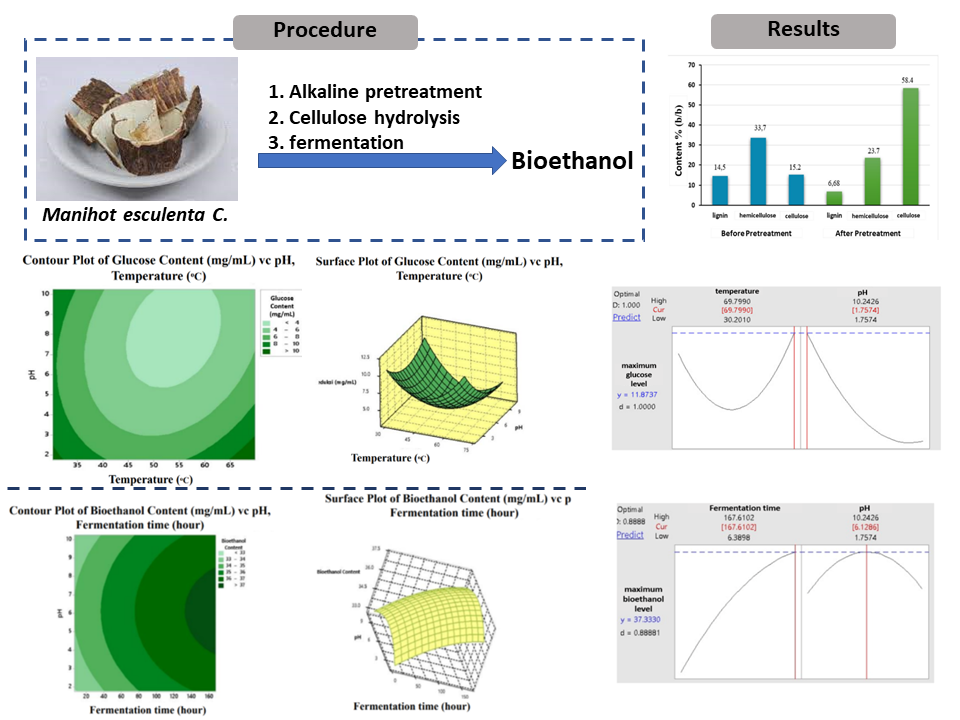
Cassava is one of the most widely produced agricultural products in Indonesia with cassava peel waste of 20%. Cassava peel contains carbohydrates and stores a high cellulose content so that it has a potential to be a bioethanol. This study aims to utilize cassava peel waste for bioethanol production with an alkaline pretreatment process, cellulase enzyme hydrolysis and fermentation by using Zymomonas mobilis bacteria. Alkaline pretreatment with 14% NaOH is used to hydrolyze lignocellulose. The hydrolysis optimization process enzymatically applies the Surface Response Method (RSM) to determine the optimum conditions at hydrolysis pH in the range of 2-10 and hydrolysis temperature in the range of 30-70 °C by analyzing glucose levels using the Dinitrosalicylic Acid (DNS) method and UV-vis spectrophotometry instruments. Surface Response Method (RSM) is likewise implemented to decide the greatest conditions of the fermentation process. The pH measurement ranges 2-10, and fermentation time takes 6 to 168 hours. Based on the results of research, it results a lignin content of 6.68% (b/b), cellulose content of 58.4% (b/b), and hemicellulose content of 27.3% (b/b). The optimum conditions of the hydrolysis process obtained an optimum glucose level of 9.22mg/mL at pH 2 and a hydrolysis temperature of 50°C. The optimum conditions of the fermentation process use Zymomonas mobilis at pH 6 while fermentation time takes 168 hours analyzed using a refractometer produced a bioethanol content of 37.75% (v/v) and a gas chromatography produced a bioethanol content of 54.94% (v/v).
References
[1] Scott, G.J., Int. J. Food Sci. Technol., 2021, 56(3), pp.1093-1114.
[2] Abidin, Z, Saraswati, E, Naid, T, Int. J. PharmTech Res., 2014, 6, 1210-1212
[3] Susanti, S., Al Karoma, D., Mulyani, D. and Masruri, M., J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2017, 6(3), p.255.
[4] Santoso, S.P, Sanjaya, N, Ayucitra, A, and Anteresti A., Indones. J. Chem. Eng., 2012, 11, 124-131.
[5] Amalia, A.V., Fibriana, F., Widiatningrum, T. and Hardianti, R.D., Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol., 2021, 35, p.102093.
[6] Yana, S., Nizar, M. and Mulyati, D., Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2022, 160, p.112268.
[7] Suhartini, S., Rohma, N.A., Elviliana, Santoso, I., Paul, R., Listiningrum, P. and Melville, L., Energy, Ecol. Environ., 2022, 7(4), pp.297-339.
[8] Popp, J., Lakner, Z., Harangi-Rákos, M. and Fari, M., Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2014, 32, pp.559-578.
[9] Akhlisah, Z.N., Yunus, R., Abidin, Z.Z., Lim, B.Y. and Kania, D., Biomass Bioenergy, 2021, 144, p.105901.
[10] Robak, K. and Balcerek, M., Microbiol. Res., 2020, 240, p.126534.
[11] Jin, Y., Lin, Y., Wang, P., Jin, R., Gao, M., Wang, Q., Chang, T.C. and Ma, H., Bioresour. Technol., 2019, 292, p.121957.
[12] Taherzadeh, M.J., and Karimi, K., Bioresources, 2007, 2, 472- 499.
[13] Albert, Idiawati, N., dan Rudiyansyah., JKK, 2015, 4, 72-75.
[14] Todhanakasem, T, Salangsing O, Koomphongse, P, Kaewket, S, Kanokratana, P, and Champreda, V., J. Frontiers Microbiol., 2019, 10, 1-9.
[15] Sabilah, L.M.Z., Mangalla, L.K., dan Imran, A.I., Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Teknik Mesin, 2020, 5, 64-68.
[16] Astuti, W., dan Susilowati, N., Jurnal Bahan Alam Terbarukan, 2015, 4, 50-54
[17] Anggraeni Y, Supriadi, dan Kasmudin, M., Journal Chemistry Academica, 2017, 6, 191-195.
[18] Maharani, D.M., Normalasari, L.N., Kumalasari, D., Prakoso, C.A.H., Kasumaningtyas, M., dan Ramadhan, M.T., AGRITECH, 2017, 37, 132-138.
[19] Chio, C., Sain, M. and Qin, W., Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2019, 107, pp.232-249.
[20] Morya, R., Kumar, M., Tyagi, I., Pandey, A.K., Park, J., Raj, T., Sirohi, R., Kumar, V. and Kim, S.H., Bioresour. Technol., 2022, 350, p.126916.
[21] Mauer, L.J. and Bradley, R.L., Moisture and total solids analysis. in Food analysis, 2017, pp.257-286.
[22] Priatna, M.R, Palit, W.H, dan Kurniawan, R., Jurnal Teknik Kimia, 2021, 1, 12-25.
[23] Suryaningrum, L.H., Nucleus Agricultural Journal, 2020, 1, 102-109.
[24] Setiadi, Mulyadi, Y, dan Kusmartono, B., Jurnal Fluida, 2017, 1, 1-17.
[25] Mulyono, A.M.W, Cahyanto, M.N, Zuprizal, and Bachruddin, Z., AGRITECH, 2009, 29(2), 53-58
[26] Nugrahini, P.N, Sitompul, H, dan Putra, D.R., Journal Analytical and Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 1, 2540-2555.
[27] Putri, S., Karakterisasi Enzim Selulase yang dihasilkan oleh Lacobacillus planturum pada Variasi Suhu, pH dan Konsentrasi Substrat, Skripsi, Jurusan Biologi, Fakultas Sains dan Teknologi, UIN Maulana Malik Ibrahim, Malang, 2016.
[28] Todhanakasem, T, Salangsing O, Koomphongse, P, Kaewket, S, Kanokratana, P, and Champreda, V., Journal Frontiers in Mocrobiology, 2019, 10, 1-9.
[29] Yang, S., Fei, Q., Zhang, Y., Contreras, L.M., Utturkar, S.M., Brown, S.D., Himmel, M.E. and Zhang, M., Microbiol Biotechnol., 2016, 9(6), pp.699-717.
[30] Hamidah, Safitri, R, dan Subroto, Jurnal Penelitian Pangan, 2016, 1, 28-35.
[31] Cazatta, M.U., 2017, Jurnal Teknik Kimia, 2017, 1, 109-211
[32] Utama, A, W, Legowo, A.M, dan Al-Baari, A.N., Jurnal Aplikasi Tekhnologi Pangan, 2013, 2, 93-100.
[33] Tse, T.J., Wiens, D.J. and Reaney, M.J., Fermentation, 2021, 7(4), p.268.
[34] Seo, H.B., Kim, H.J., Lee, O.K., Ha, J.H., Lee, H.Y. and Jung, K.H., J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2009, 36(2), pp.285-292.
Refbacks

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.