Preparation and characterization of poly-(methacrylatoethyl trimethylammonium chloride-co-vinylbenzyl chloride-co-ethylene dimethacrylate) monolith
Abstract
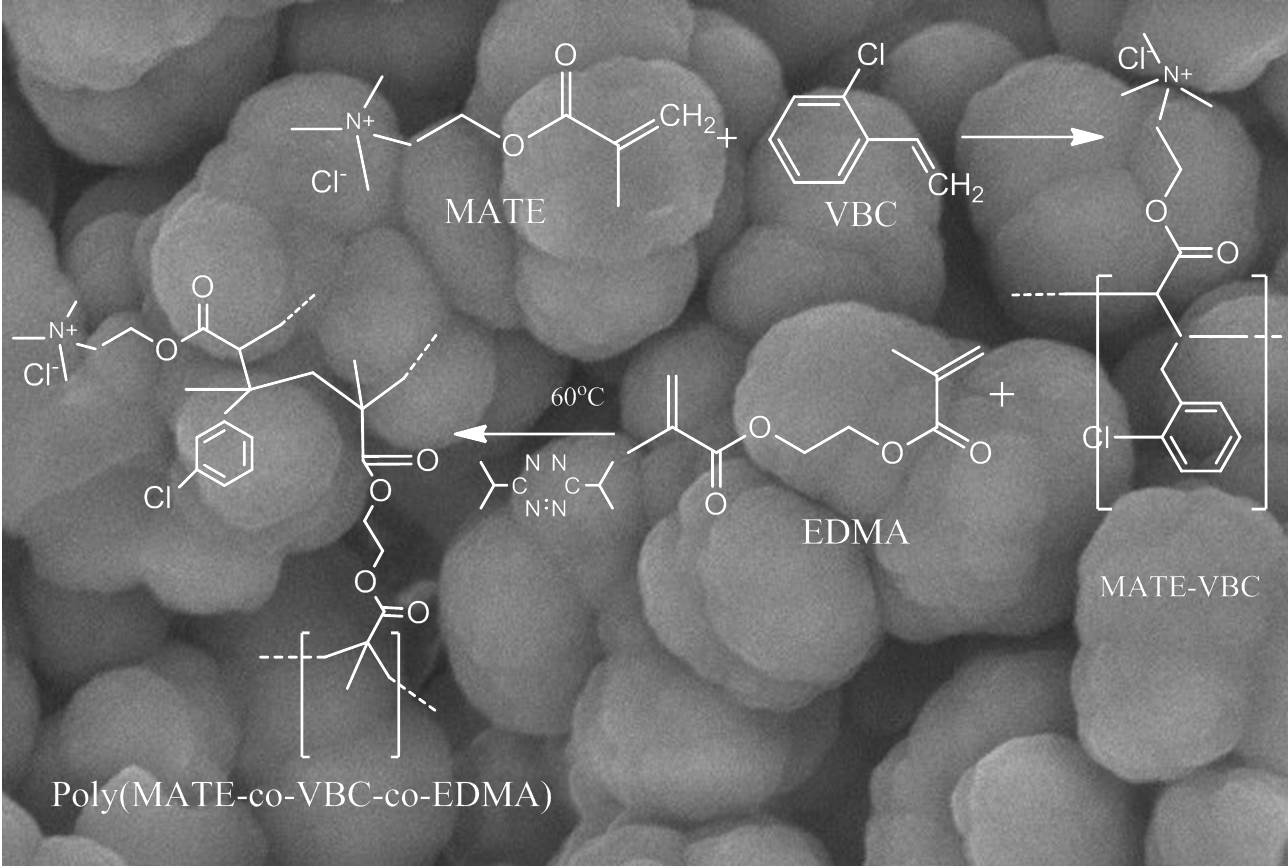
A polymer monolithic column, poly-(methacrylatoethyltrimethylammonium chloride-co-vinylbenzyl chloride-co-ethylene dimethacrylate) or poly-(MATE-co-VBC-co-EDMA) was successfully prepared in the current study by one-step thermally initiated in situ polymerization, confined in a steel tubing of 0.5 mm i.d. and 1/16” o.d. The monoliths were prepared from methacrylatoethyltrimethylammonium chloride (MATE) and vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) as monomer and ethylene dimethacrylate (EDMA) as crosslinker using a binary porogen system of 1-propanol and 1,4-butanediol. The inner wall of steel tubing was pretreated with 3-methacryloxypropyl-trimethoxysilane (MAPS). In order to obtain monolith with adequate column efficiency and low flow resistance, some parameters such as total monomer concentration (%T) and crosslinker concentration (%C) were optimized. The morphology of this monolith was assessed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The properties of the monolithic column, such as permeability, binding capacity, and pore size distribution were also characterized in detail. From the results of the characterization of all monolith variation, monolith with %T 30 %C 50 and %T 35 %C 50 give the best characteristic. These monoliths have high permeability, adequate molecular recognition sites (represented with binding capacity value of over 20 mg/mL), and have over 80% flow through pores in their pore structure contribute to low flow resistance. The resulted monolithic columns have promising potential for dual mode liquid chromatography. MATE may contribute for anion-exchange while VBC may responsible for reversed-phase liquid chromatography.
References
R.D. Arrua, M. Talebi, T.J. Causon, E.F. Hilder, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2012, 738, 1-12. [2] S. Hjertén, J.L. Liao, R. Zhang, J. Chromatogr. A., 1989, 473, 273-275. [3] J.L. Liao, R. Zhang, S. Hjertén, J. Chromatogr. A., 1991, 586, 21-26. [4] S. Hjertén, Y.Y.M. Li, J.L. Liao, J. Mohammad, K. Nakazato, G. Pettersson, Nature, 1992, 810-811. [5] F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, Anal. Chem., 1992, 64, 820-822. [6] Q.C. Wang, F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, J. Chromatogr. A., 1994, 669, 230-235. [7] F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, J. Chromatogr. A., 1995, 702, 89-95. [8] M. Barut, A. Podgornik, L. Urbas, B. Gabor, P. Brne, J. Vidič, S. Plevčak, A. Štrancar, J. Sep. Sci., 2008, 31, 1867–1880. [9] A. Podgornik, S. Yamamoto, M. Peterka, N. L. Krajnc, J. Chromatogr. B., 2013, 927, 80-89. [10] T. Nema, E.C.Y. Chan, P.C. Ho, J. Pharmaceut. Biomed., 2014, 87, 130-141. [11] Y. Ueki, T. Umemura, J. Li, T. Odake, K. Tsunoda, Anal. Chem., 2004, 76, 7007-7012. [12] D. Schaller, E.F. Hilder, P.R. Haddad, J. Sep. Sci., 2006, 29, 1705-1719. [13] T. Umemura, Y. Ueki, K. Tsunoda, A. Katakai, M. Tamada, H. Haraguchi, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2006, 386, 566-571. [14] M. Guerrouache, B. Carbonnier, C. Vidal-Madjar, M.C. Millot, J. Chromatogr. A., 2007, 1149, 368-376. [15] I. Gusev, X. Huang, C. Horváth, J. Chromatogr. A., 1999, 855, 273-290. [16] D. Lee, F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, J. Chromatogr. A., 2004, 1051, 53-60. [17] Y. Ueki, T. Umemura, Y. Iwashita, T. Odake, H. Haraguchi, K. Tsunoda, J. Chromatogr. A., 2006, 1106, 106-111. [18] J. Vidič, A. Podgornik, J. Jančar, V. Frankovič, B. Košir, N. Lendero, K. Čuček, M. Krajnc, A. Štrancar, J. Chromatogr. A., 2007, 1144, 63–71. [19] A. Korolev, E. Victorova, T. Ibragimov, A. Kanatyeva, A. Kurganov, J. Sep. Sci., 2012, 35, 957–963. [20] E.C. Peters, M. Petro, F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, Anal. Chem., 1997, 69, 3646-3649. [21] B. Carbonnier, M. Guerrouache, R. Denoyel, M.C. Millot, J. Sep. Sci., 2007, 30, 3000–3010. [22] S. Eeltink, F. Svec, Electrophoresis, 2007, 28, 137–147. [23] J. Urban, P. Jandera, J. Sep. Sci., 2008, 31, 2521–2540. [24] I. Nischang, O. Brüggemann, J. Chromatogr. A., 2010, 1217, 5389-5397. [25] J. Urban, F. Svec, J.M.J. Fréchet, J. Chromatogr. A., 2010, 1217, 8212-8221. [26] X. Chen, H.D. Tolley, M.L. Lee, J. Chromatogr. A., 2011, 1218, 4322-4331. [27] X. Huang, Q. Wang, H. Yan, Y. Huang, B. Huang, J. Chromatogr. A., 2005, 1062, 183-188. [28] Z. Xu, L. Yang, Q. Wang, J. Chromatogr. A., 2009, 1216, 3098-3106. [29] E.P. Nesterenko, P.N. Nesterenko, D. Connolly, F. Lacroix, B. Paull, J. Chromatogr. A., 2010, 1217, 2138-2146. [30] S. Shu, H. Kobayashi, N. Kojima, A. Sabarudin, T. Umemura, J. Chromatogr. A., 2011, 1218, 5228-5234. [31] A. Sabarudin, J. Huang, S. Shu, S. Sakagawa, T. Umemura, Anal. Chim. Acta., 2012, 736, 108-114. [32] S. Shu, H. Kobayashi, M. Okubo, A. Sabarudin, M. Butsugan, T. Umemura, J. Chromatogr. A., 2012, 1242, 59-66. [33] M.L. Chen, Y.L. Liu, X.W. Xing, X. Zhou, Y.Q. Feng, B.F. Yuan, Chem. Eur. J., 2013, 19, 1035–1041. [34] M. Al-Bokari, D. Cherrak, G. Guiochon, J. Chromatogr. A., 2002, 975, 275-284. [35] P. Jandera, J. Urban, V. Škeříková, P. Langmaierm, R. Kubíčková, J. Planeta, J. Chromatogr. A., 2010, 1217, 22-33.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.