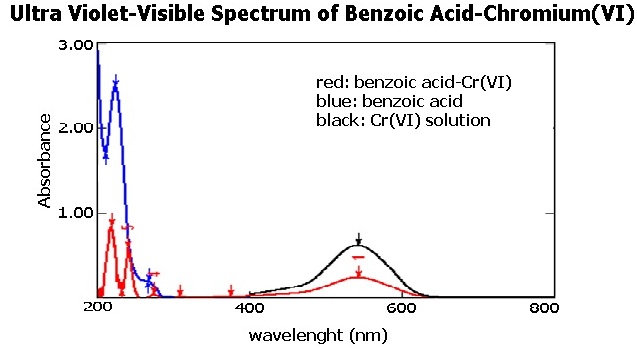
The Ability of Benzoic Acid to Reduce Cr(VI) Heavy Metal Content in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
References
Januarita, R., dan Hardiansyah, Indon. J. Chem., 2003, 3 (3), 169-175. [2] Aji, B.K., dan Kurniawan, F., Jurnal Sains POMITS, 2012, 1 (1), 1-6. [3] Mukarromah, L., Efektifitas Bioflokulan Biji Kelor (Moringa oleifera Lamk.) dalam Mengurangi Kadar Cr(VI), Undergraduate Thesis (Skripsi), Fakultas Sains dan Teknologi, Universitas Islam Negeri Malang, Indonesia, 2008. [4] DARJITO, Darjito; PURWONUGROHO, Danar; NINGSIH, Rumiati. J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2014, 3.2: 53-61. [5] SABARUDIN, Akhmad; MOTOMIZU, Shoji. J. Pure App. Chem. Res., 2013, 2.1: 48-54. [6] Di Natale, F., Erto, A., Lancia, A., & Musmarra, D. J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 281, 47-55. [7] Maleki, A., Hayati, B., Naghizadeh, M., & Joo, S. W. J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2015, 28, 211-216. [8] Song, Z., Li, W., Liu, W., Yang, Y., Wang, N., Wang, H., & Gao, H., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(17), 13028-13035. [9] Li, L., Li, Y., Cao, L., & Yang, C., Carbohyd. Polym., 2015, 125, 206-213. [10] KUMAR, A. Santhana Krishna; JIANG, Shiuh-Jen; TSENG, Wei-Lung., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3.13: 7044-7057. [11] KUMARI, Madhu; PITTMAN, Charles U.; MOHAN, Dinesh, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 442: 120-132. [12] Hokkanen, S., Bhatnagar, A., Repo, E., Lou, S., & Sillanpää, M., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 283, 445-452. [13] Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Qiao, W., Long, D., & Ling, L., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, 462, 200-207. [14] Ma, L., Xi, Y., He, H., Ayoko, G. A., Zhu, R., & Zhu, J., App. Clay Sci., 2016, 120, 9-15. [15] Wu, Y., Fan, Y., Zhang, M., Ming, Z., Yang, S., Arkin, A., & Fang, P., Biochem. Eng. J., 2016, 105, 27-35. [16] Ismangil and Hanudin, E., Jurnal Ilmu Tanah dan Lingkungan, 2005, 5 (1), 1-17. [17] Chipley, J. R., Sodium Benzoate and Benzoic Acid, Antimicrobials in Food, 3rd edition, 2005, CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton. [18] Sastrohamidjojo, H., Spektroskopi, 1987, PT Liberty, Yogyakarta. [19] LEWANDOWSKI, Włodzimierz. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 1988, 17.1: 131-138.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.