L-Histidine-Modified Silica from Rice Husk and Optimization of Adsorption Condition for Extractive Concentration of Pb(II)
Abstract
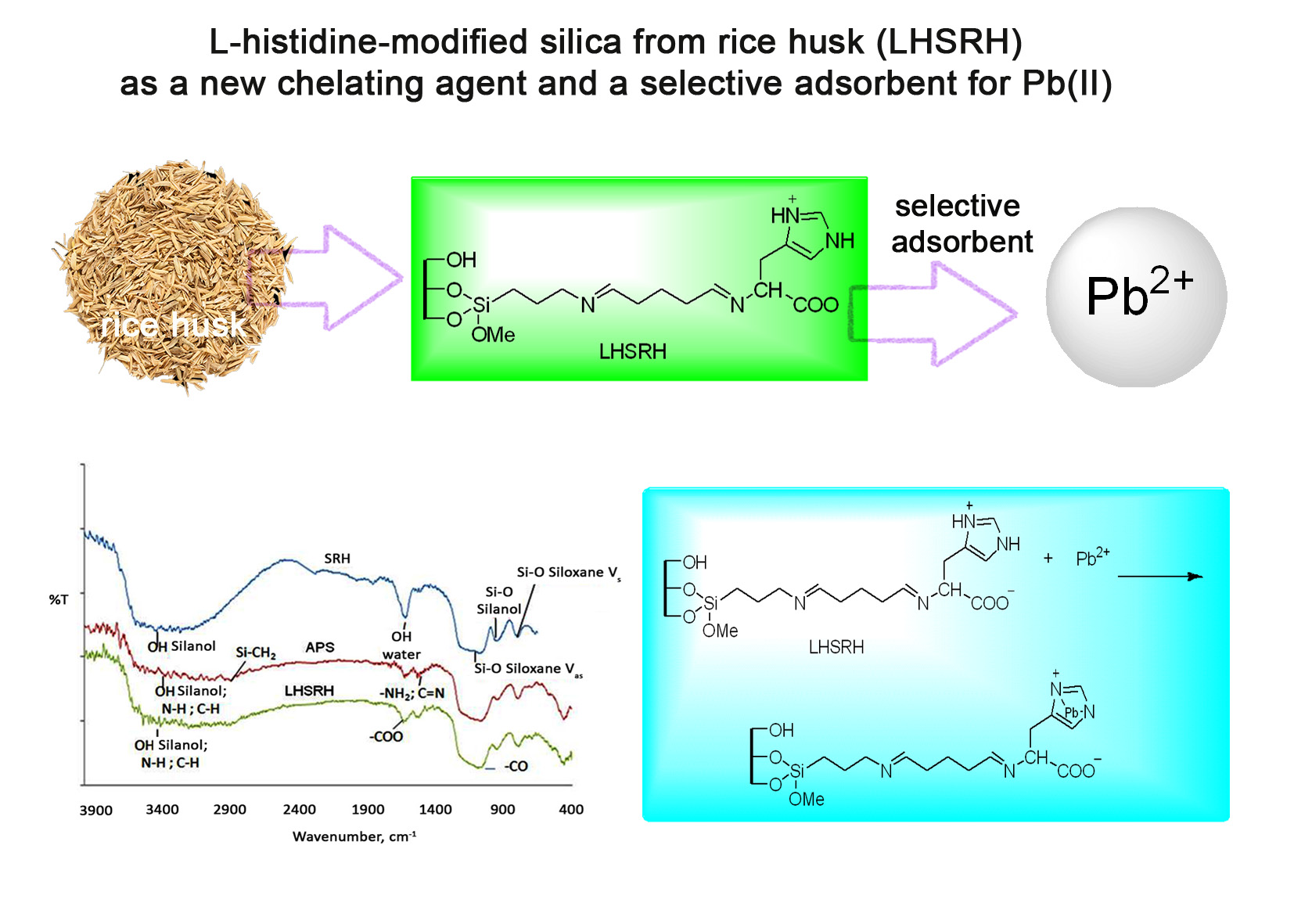
A new chelating agent, L-histidine-modified silica from rice husk (LHSRH), was prepared to increase the adsorption capacity and selectivity for Pb(II). LHSRH was synthesized by immobilizing L-histidine on silica from rice husk (RH) modified with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS). Silica from rice husk (SRH) was synthesized via precipitation process by adding hydrochloric acid solution to rice husk ash (RHA). The RHA was subsequently destructed with sodium hydroxide and heated to obtain sodium silicate (Na2SiO3). SRH was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and x-ray diffraction. The LHSRH was used further to adsorp Pb(II) metal ion. The pH range, amount of adsorbent, and adsorption time were optimized by response surface methodology. The optimum condition for the adsorption of Pb(II) was pH 5, an amount of adsorbent 0.1 g; and adsorption time 15 minutes. The adsorption capacity for Pb(II) ion was found to be 62.5 mg/g. The adsorption behavior of the matrix followed the Langmuir’s model.
References
[1] Manahan S.E., Fundamentals of Environmental Chemistry, 2001, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
[2] Niu Y., Qu R., Sun C., Wang C., Chen H., Ji C., Zhang Y., Shao X., and Bu F., J. Hazard. Mater., 2013, 244-245, 276-286.
[3] Environmental Protection Agency-USA, Lead Renovation, Repair, and Painting Program Rules. https://www.epa.gov/lead/renovation-repair-and-painting-program. Accessed date 5 January 2018.
[4] Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Nomor 492 Tahun 2010 tentang Persyaratan Kualitas Air Minum, 2010, Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia, Jakarta.
[5] Ghaedi M., and Sharifpour E., Desalin. Water Treat., 2012, 41, 315-324.
[6] Zhu X., Cui Y., Chang X., Zou X., and Li Z., Microchim Acta, 2008, 164, 125-132.
[7] Radi S., Tighdouini S., Bacquet M., Degoutin S., Cazier F., Zaghrioui M., and Mabkhot Y.N., Molecules, 2014, 19, 247-262.
[8] Kalaphaty U., Proctor A., and Schultz J., Bioresour. Technol., 2000, 73, 257-262.
[9] Mujiyanti D.R., Nuryono, and Kunarti E.S., J. Sains Terapan Kim., 2010, 4(2), 150-167.
[10] Ghosh R., and Bhattacherjee S., J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol., 2013, 4(4), 156-168.
[11] Rohaeti E., Hikmawati, and Irzaman, Production of semiconductor materials silicon from silica rice husk waste as alternative silicon sources. Proceeding of the International Conference on Materials Science and Technology 19-23 October, 2010, page 265-272. ISBN 978-602-97444-3-9. Indonesian National Nuclear Energy Agency Republic of Indonesia, Serpong,
[12] Yu W., Xia C., Sheng-Chao Y., Qing-Hui L.V., Fang-Gui Y., and Shu-Lin Z., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2014, 42(4), 495-500.
[13] Roat-Malone R.M., Bioinorganic Chemistry, 2nd edition, 2007, John Wiley & Son, Chestertown.
[14] Djatmiko R., and Amaria, UNESA J. Chem., 2012, 1(2), 58-65.
[15] Vejayakumaran P., Rahman I.A., Sipaut C.S., Ismail J., and Chee C.K., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2008, 328, 81-91.
[16] Malachowski L., and Holcombe J.A., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2003, 495, 151-163.
[17] Javadian H., Koutenaei B.B., Khatti R., and Toosi M., J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2014, 21(S1), S219-S230.
[18] Jiang N., Chang X., Zheng H., He Q., and Hu Z., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, 577, 225-231.
[19] Silverstein R.M., Webster F.X., Kiemle D.J., Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compound, 7th edition, John Wiley & Son, New York.
[20] Ghorbani M., Nowee S.M., Ramezanian N., Raji F., Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 161, 117-126.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.