The Effect of Bacterioruberin Deletion on Production of Bacteriorhodopsin in Halobacterium salinarum R1
Abstract
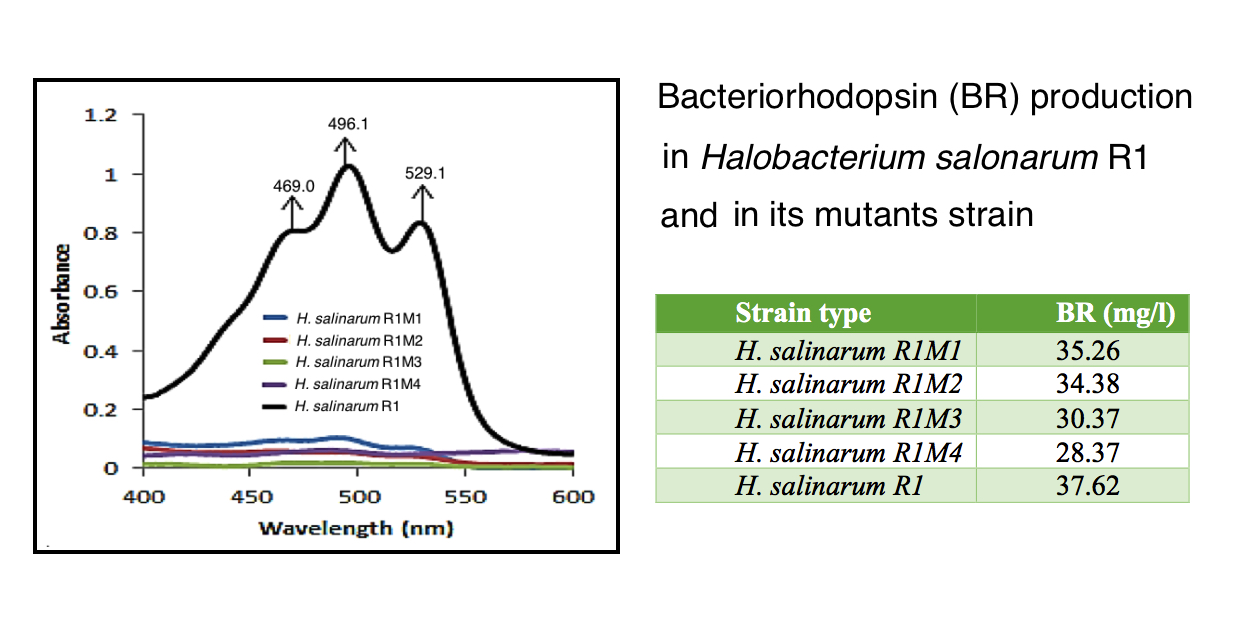
Bacteriorhodopsin is a retinal protein located in purple membrane of Halobacterium salinarum which acts as light-dependent proton pump. Bacterioruberin is a by-product in bacteriorhodopsin biosynthesis pathway in Halobacterium salinarum. In order to study the effects of bacterioruberin deletion on quantity of active cellular bacteriorhodopsin production, random mutation by UV radiation on Halobacterium salinarum R1 has been carried out. Afterwards, mutated strains which lacked bacterioruberin were selected and production of cellular active bacteriorhodopsin in both mutated and normal (with bacterioruberin) strains were evaluated. The results of this study indicated that the bacterioruberin deletion had insignificant effects on bacteriorhodopsin production. Hence, the biosynthesis pathway of bacteriorhodopsin basically has to be considered independently from the bacterioruberin synthesis.
References
Gonzalez, O., S. Gronau, M. Falb, F. Pfeiffer, E. Mendoza, R. Zimmer, and D. Oesterhelt, Mol Biosyst, 2008, 4, 148-159. website
[2] J. Twellmeyer, A. Wende, J. Wolfertz, F. Pfeiffer, M. Panhuysen, A. Zaigler, J. Soppa, G. Welzl, D. Oesterhelt, PLoS, 2007, 10, 1-9. crossref
[3] J. K. Lanyi, H. Luecke, Curr Opin Struct Biol., 2001, 11(4), 415-419. crossref
[4] Dummer A.M., Bonsall J.C., Cihla J.B., Lawry S.M., Johnson G.C., Peck R.F., J Bacteriol, 2011, 193(20), 5658-5667. website
[5] Aharon Oren, David R. Arahal, Antonio Ventosa, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2009, 59, 637-642. website
[6] S. Machmudah, Y. Kawahito, M. Sasaki, M. Goto, J Supercrit Fluids. 2008, 44(3), 308-314. crossref
[7] Davies B. H. In: T. W. Goodwin, ed., 1965, Chemistry and Biochemistry of Plant Pigments, Academic Press, London. pp. 489-532.
[8] Richard F., Betlach M.C., J Bacteriol., 1994, 76(6), 1655–1660. website
[9] Shand R.F., Betlach M.C. J Bacteriol, 1991, 173, 4692-4699. website
[10] M. Ahmadi, N. Lunscher, J. T. W. Yeow, Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B., 2013, 300, 30-34. crossref
[11] Rehorek M., Heyn M.P., Biochemistry, 1979, 18, 4977-4983. website
[12] McCready S., Mutant Res., 1996, 364, 25–32. crossref
[13] McCready S., Marcello L. Biochem Soc Trans., 2003, 31, 694–698. website
[14] Sebastian B., Thorsten A., Gabi S., PLoS, 2000, 1, 92-97. website
[15] Asgarnai E., Teroto H., Asagoshi K., Shahmohammadi H. R., Ohyama Y., Saito T., Yamamoto O., Ide H., J Radiat Res, 2000, 41, 19–34. website
[16] Shahmohammadi H.R., Asgarani E., Terato H., Saito T., Ohyama Y., Gekko K., Yamamoto O., Ide, H., J Radiat Res., 1998, 39, 251–262. website
[17] Kottemann M., Kish A., Iloamrsi C., Bjork S., Diruggiero, J Extremophiles., 2005, 9, 219-227. website
[18] C. P. Marshall, S. Leuko, C. M. Coyle, M. R. Walter, B. P. Burns, and B. A. Neilan. Astrobiology, 2007, 7(4), 631-643. website
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.