Metabolite Variation of Peanut Hulls (Arachis hypogaea L.) from Three Locations of Lombok Island on the Basis of GC-MS Analysis
Abstract
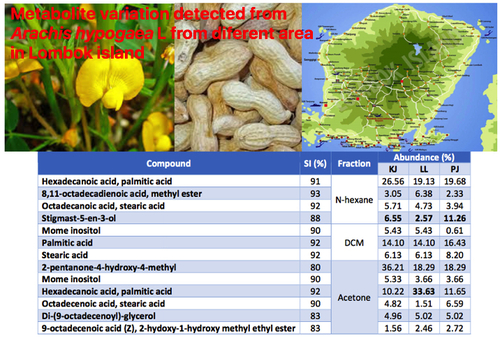
This article is a part of studies to investigate the potential of natural products from Lombok Island for antidiabetic agents. This study was directed to learn the metabolite variations of peanut hulls collected from three different locations in Lombok Island. The hull samples were extracted in methanol, followed by partition process into three fractions using three solvents with varied polarities (dichloromethane, hexane and acetone). The fractions were then separated and identified for their chemical composition by using GC-MS instrument. Metabolite variations of three extracts showed that the antidiabetic compounds stigmast-5-en-3-ol and oleic acid were found in all three locations with different percentages of abundance. Another antidiabetic compound, linoleic acid, was only identified in peanut hulls from the village of Pringga Jurang (PJ). Besides the antidiabetic compounds, there were other major compounds with known biological activities discussed to find other uses of the hulls.
References
[1] Bilbis, L. S., Shehu, R. A., & Abubakar M. G., Phytomedicine, 2002, 9(6), 553-555.
[2] Kumar, S., Kumar, V., & Prakash, O., BioMed Res. Int., 2013, 1-7.
[3] Karan, S. K., Mishra, S. K., Pal, S., & Mondal, A., J. Med. Plants Res., 2012, 6(7), 1219-1223.
[4] Gupta, R., Sharma, A. K., Dobhal, M. P., Sharma, M. C., & Gupta, R. S., Journal of Diabetes, 2011, 3(1), 29-37.
[5] Ahmad, Z., Zamhuri, K. F., Yaacob, A., Siong, H. C., Selvarajah, M., Ismail, A., & Hakim, M. N., Molecules, 2012, 17(8), 9631-9640.
[6] Houseknecht, K. L., Vanden, H. J. P., Moya-Camarena, S. Y., Portocarrero, C. P., Peck, L. W., Nickel, K. P., et al., Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1998, 244, 678-682.
[7] Vassiliou, E. K., Gonzalez, A., Garcia, C., Tadros, J. H., Chakraborty, G., & Toney, J. H., Lipids Health Dis, 2009, 8(25).
[8] Rosa, Jagoda & Rosa Josip, Diabetol Croat, 2004, 33(1), 17-21.
[9] Saeidnia, S., Manayi, A., Gohari, A. R., & Abdollahi, M., European J Med Plants, 2014, 4(5), 590-609.
[10] Carrillo, C. M., Cavia, d. M., & Alonso-Torre, S. R., Nutr Hosp, 2012, 27(5), 1860-1865.
[11] Melariri, P., Campbell, W., Etusim, P., & Smith, P., Adv Stud Biol, 2012, 4(3), 333-349.
[12] Dewick, P. M., Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 2009, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, New Jersey.
[13] Kunst, L., & Samuels, A. L., Prog Lipid Res, 2003, 42, 51-80.
[14] Velíšek, J., & Cejpek, K., Czech J Food Sci, 2006, 24(5), 193-216.
[15] Manilal, A., Sujith, S., Sabarathnam, B., Kiran, G. S., Selvin, J., Shakir, C., et al., Acta Bot Croat, 2011, 70(1), 81-90.
[16] McGaw, L. J., Jager, A. K., & Van Staden, J., Fitoterapia, 2002, 73(5), 431-433.
[17] Harada, H., Yamashita, U., Kurihara, H., Fukushi, E., Kawabata, J., & Kamei, Y., Anticancer Res, 2002, 22(5), 2587-2590.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.